- Home
-
Screening
- Ionic Screening Service
-
Ionic Screening Panel
- Ligand Gated Ion Channels
- Glycine Receptors
- 5-HT Receptors3
- Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors
- Ionotropic Glutamate-gated Receptors
- GABAa Receptors
- Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulators (CFTR)
- ATP gated P2X Channels
- Voltage-Gated Ion Channels
- Calcium Channels
- Chloride Channels
- Potassium Channels
- Sodium Channels
- ASICs
- TRP Channels
- Other Ion Channels
- Stable Cell Lines
- Cardiology
- Neurology
- Ophthalmology
-
Platform
-
Experiment Systems
- Xenopus Oocyte Screening Model
- Acute Isolated Cardiomyocytes
- Acute Dissociated Neurons
- Primary Cultured Neurons
- Cultured Neuronal Cell Lines
- iPSC-derived Cardiomyocytes/Neurons
- Acute/Cultured Organotypic Brain Slices
- Oxygen Glucose Deprivation Model
- 3D Cell Culture
- iPSC-derived Neurons
- Isolation and culture of neural stem/progenitor cells
- Animal Models
- Techinques
- Resource
- Equipment
-
Experiment Systems
- Order
- Careers
HCN1 & HCN4
HCN1 & HCN4 belong to the ion channel family of hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated (HCN) cation channels. Upon hyperpolarization, both generate a characteristic inward current which shows the typical properties of the conductance coined If in the heart and Ih in the brain.
HCN1 is the fastest activating channel with an activation constant τ in the range of 30 - 300ms, whereas HCN4 represents the most slowly activating isoform with τ between 300ms.
HCN1 (Potassium/sodium hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated channel 1) is widely expressed such as in the sinoatrial node, the neocortex, hippocampus, cerebellar cortex, dorsal root ganglion, trigeminal ganglion and brainstem. HCN1 exhibits weak selectivity for potassium over sodium ions. Contributes to the native pacemaker currents in heart (If) and in neurons (Ih).
HCN4 (Potassium/sodium hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated channel 4) is prominently expressed in the pace maker region of the mammalian heart and contributes to the native pacemaker currents in heart. It is a hyperpolarization-activated ion channel with very slow activation and inactivation exhibiting weak selectivity for potassium over sodium ions. Some humans with bradycardia and Sick sinus syndrome have been shown to have mutations in their HCN4 gene. The role of HCN channels in autonomic control of heart rate is currently a matter of ongoing investigation.
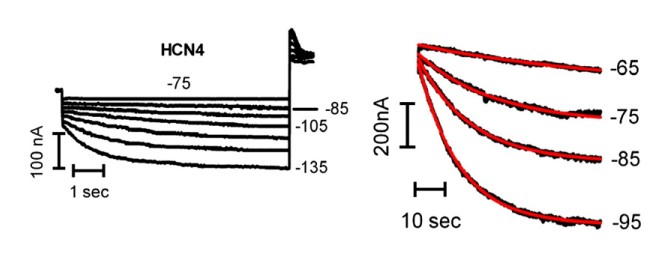
Fig. 1 Functional expression of HCN4 in Xenopus oocytes.
Staffed with a group of experts that have gained years of experience in ion channel safety assays and cardiotoxicity assessment, Creative Bioarray offers assays for HCN1&4 channels to evaluate compound cardiovascular safety and to support drug development.
References
Herrmann S, et al. HCN channels—modulators of cardiac and neuronal excitability. Int J Mol Sci.2015; 16: 1429–1447.
Zhang Q, et al. Associated changes in HCN2 and HCN4 transcripts and If pacemaker current in myocytes. BBA – Biomembranes. 2009; 1788: 1138–1147.
Related Section
Inquiry

