- Home
-
Screening
- Ionic Screening Service
-
Ionic Screening Panel
- Ligand Gated Ion Channels
- Glycine Receptors
- 5-HT Receptors3
- Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors
- Ionotropic Glutamate-gated Receptors
- GABAa Receptors
- Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulators (CFTR)
- ATP gated P2X Channels
- Voltage-Gated Ion Channels
- Calcium Channels
- Chloride Channels
- Potassium Channels
- Sodium Channels
- ASICs
- TRP Channels
- Other Ion Channels
- Stable Cell Lines
- Cardiology
- Neurology
- Ophthalmology
-
Platform
-
Experiment Systems
- Xenopus Oocyte Screening Model
- Acute Isolated Cardiomyocytes
- Acute Dissociated Neurons
- Primary Cultured Neurons
- Cultured Neuronal Cell Lines
- iPSC-derived Cardiomyocytes/Neurons
- Acute/Cultured Organotypic Brain Slices
- Oxygen Glucose Deprivation Model
- 3D Cell Culture
- iPSC-derived Neurons
- Isolation and culture of neural stem/progenitor cells
- Animal Models
- Techinques
- Resource
- Equipment
-
Experiment Systems
- Order
- Careers
Neurotransmission Functions
Of all major treatment areas, Central Nervous System (CNS) is the one with the lowest satisfaction. Most major CNS diseases have restricted pharmacology treatment options. For example, major neurodegenerative diseases (Alzheimer's disease (AD) and Parkinson's disease (PD)), there are no treatments that reverse or even delays disease progression. Treatment options for symptoms are limited and only small subset of symptoms are managed, and many treatments work only in a small portion of the population, and/or in a limited period of time during the progression of the disease. Although many new options have been made to improve the ability to treat central nervous system diseases, researchers have achieved limited success. Drugs are often associated with significant side effects in the treatment of CNS diseases, which may further complicate the progression of the disease. In fact, in many cases, secondary medications are designed to treat side effects. Overall, these challenges have established the necessary data platforms in advancing drugs to clinical trials treating CNS diseases.
The development of effective, new therapeutics for the majority of CNS diseases is challenged by the neuronal diversity and connectivity of the brain. For drugs targeting neuronal cells, simply testing individual neuronal physiological properties is not enough. Neuronal transmission functions should be evaluated on both in vitro and in vivo levels. This level of complexity requires an understanding of organizational principles and cell-type specificity.
Creative Bioarray offers a series of in vitro electrophysiological assays to directly measure the neuronal activity of a single cell or channel (receptor) and also to quantify synaptic inputs of the excitatory/inhibitory circuits from the tissue obtained from living animals. We have extensive experience in investigating efficacy and function in the central and peripheral nervous systems in isolated models.
Designed to assess the neurotoxic, addictive or sedative potential of a compound on the CNS, Creative Bioarray screening includes a general CNS explorer panel, and to memory, pain and anti-epilepsy, our panels enabling drug development programs to establish undesirable side effects sooner. This helps in evaluating seizure risk, drug induced cognitive dysfunction risk, dorsal root ganglia responses or nerve conduction effects. These assays have been developed, and are offered, in several preclinical animal models such as the mouse, rat, minipig, dog and non-human primate to allow species comparison.
Electrophysiology and functional connectomics are key tools in elucidating the mechanisms of action underlying the pathophysiology of CNS disorders and facilitating the development of new therapeutics. Accordingly, we support preclinical research and development programs in the areas of neurodegeneration, neurocognition and functional connectomics by providing electrophysiological characterization of compounds with a focus on target engagement, efficacy and potency in multiple levels including cultured neurons and brain slices.
Highlights
Creative Bioarray has unparalleled expertise in performing whole-cell current-clamp and voltage-clamp recordings from isolated preparations of the nervous system. The recordings are a valuable tool in the study of synaptic plasticity, which is thought to underlie learning, memory and some brain pathologies. Up- or down-regulation of synaptic transmission can shed light on cellular and network mechanisms of numerous CNS diseases, including Alzheimer's disease, autism and ataxia. We take pride in using these techniques to determine mechanism of action.
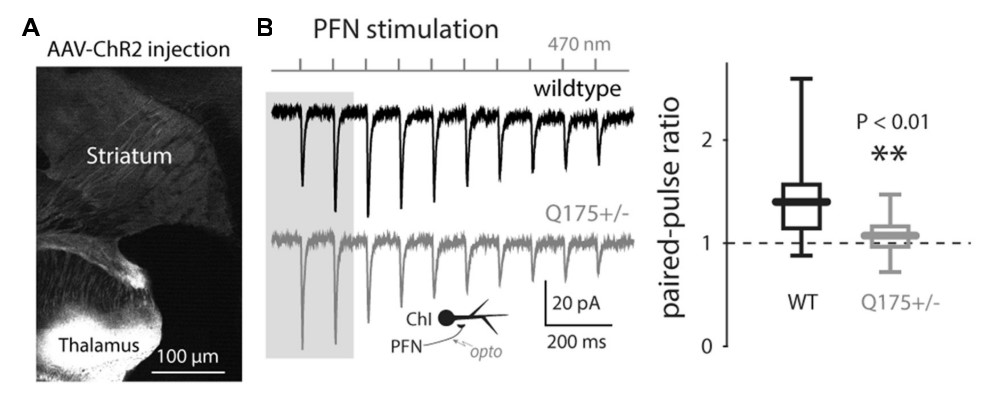
Fig. 1 Light-driven paired-pulse ratios (PPRs) of thalamo- and cortico-striatal synapses onto ChIs in the Q175 (PD model) mouse
Creative Bioarray has been studying neural circuits using multiple techniques (including whole cell, perforated patch and extracellular recordings) for the past decade. We have a wealth of experience in performing mechanistic and efficacy studies using almost all the commonly studied pathways in the hippocampus and other brain regions in isolated rodent tissue. Multiple different regions and pathways are set as experiment models in Creative Bioarray (CA1/3, DG, PFC; Sciatic nerve-DRG-dorsal root preparation etc.).
Electrophysiological recordings from brain slices are a direct way to probe neural function, detect pathological functional abnormalities and explore sensitivity of spontaneous and evoked electrical signal transmissions to drugs. Rodent brain slices with a preserved brain architecture, maintain functional local synaptic circuitry which allow precise control of the extracellular environment and performing drug test. Based on recordings on brain slices, we offer analysis of synaptic evoked and spontaneous synaptic currents/potentials, their biophysical properties, facilitation and depression, analysis of agonist/antagonist evoked postsynaptic current, analysis of input/output properties, evaluation of the function of feedback and feedforward inhibitory network motifs
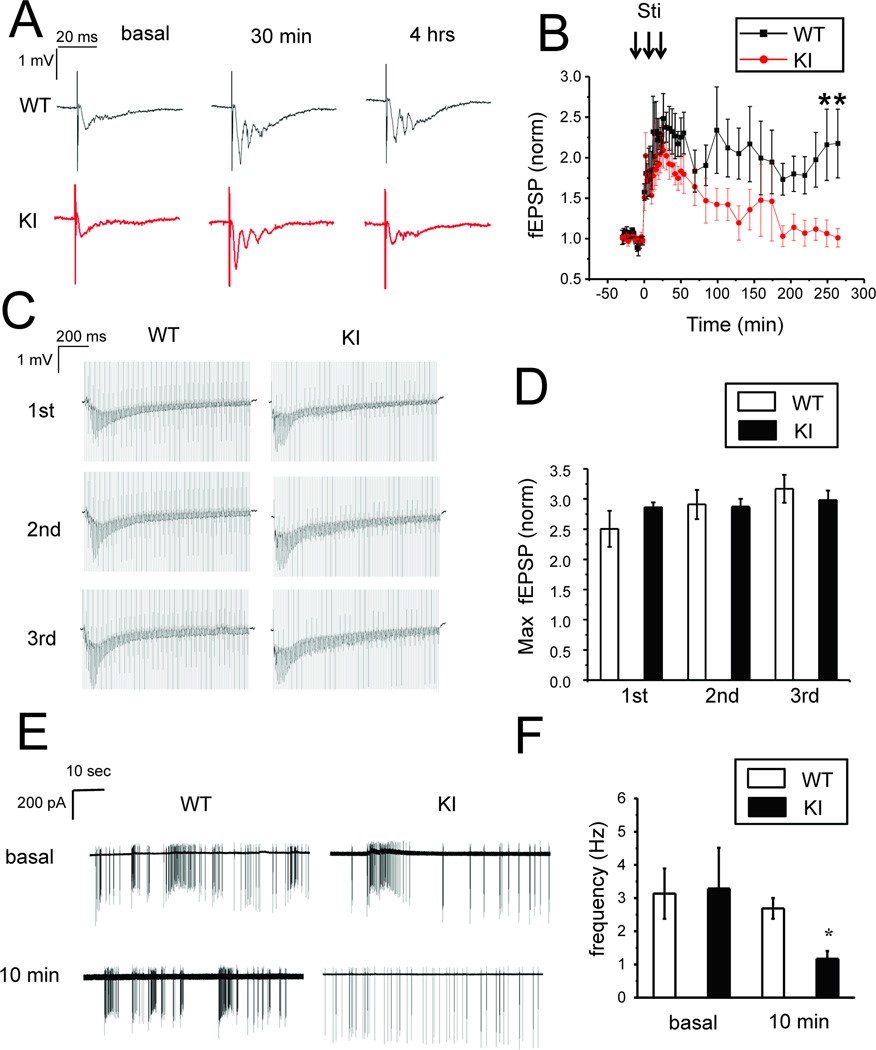
Fig.2 L-LTP defects in KI (AD model) hippocampal slices
Test Items
Pre-/Postsynaptic Mechanism
Miniature Postsynaptic Potentials
LTP & LTD Formation or Deficit Detection
Synaptic Plasticity: LTP/LTD, HFS and TBS
Disease Model: LTP deficits with Aβ, α-synuclein
Populational Spikes Recordings
Paired-pulse Ratio Recordings
Paired Coupled Recordings
GAP Junctions
Paired-Pulse Depression
Paired-Pulse Facilitation
Basal Synaptic Transmission Recordings
Baseline Synaptic Function: I/O analysis
Input Mechanism
Electrically /Pharmacologically-evoked Postsynaptic Potentials
Assays mechanisms & Techniques
All above assays are done on acute/cultured organotypic brain slices. Some will be tested on acutely isolate dissociated neurons (hippocampal neurons, DRG…) or primary cultured neurons or iPSC-derived neurons. Using conventional manual patch-clamp techniques. Calcium signaling test will be tested on cultured neurons or brain slices using Ca2+ sensitive indicators.
Customized Service
Expert electrophysiologists of Creative Bioarray will be able to design an assay to meet your requirements.
Quotation and Ordering
If you have any special needs in our Neurotransmission Functions Service, please contact us at Email or Telephone for this special service. Let us know what you need and we will accommodate you. We look forward to working with you in the future.
References
Zhang, H., et al. Calcium signaling, excitability, and synaptic plasticity defects in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. J. Alzheimers. Dis. 2015; 45: 561–580.
Tanimura, A., et al. Cholinergic Interneurons Amplify Corticostriatal Synaptic Responses in the Q175 Model of Huntington's Disease. Front. Syst. Neurosci. 2016; 10: 102.
Related Section
Inquiry

