- Home
-
Screening
- Ionic Screening Service
-
Ionic Screening Panel
- Ligand Gated Ion Channels
- Glycine Receptors
- 5-HT Receptors3
- Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors
- Ionotropic Glutamate-gated Receptors
- GABAa Receptors
- Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulators (CFTR)
- ATP gated P2X Channels
- Voltage-Gated Ion Channels
- Calcium Channels
- Chloride Channels
- Potassium Channels
- Sodium Channels
- ASICs
- TRP Channels
- Other Ion Channels
- Stable Cell Lines
- Cardiology
- Neurology
- Ophthalmology
-
Platform
-
Experiment Systems
- Xenopus Oocyte Screening Model
- Acute Isolated Cardiomyocytes
- Acute Dissociated Neurons
- Primary Cultured Neurons
- Cultured Neuronal Cell Lines
- iPSC-derived Cardiomyocytes/Neurons
- Acute/Cultured Organotypic Brain Slices
- Oxygen Glucose Deprivation Model
- 3D Cell Culture
- iPSC-derived Neurons
- Isolation and culture of neural stem/progenitor cells
- Animal Models
- Techinques
- Resource
- Equipment
-
Experiment Systems
- Order
- Careers
KCNQ1/mink/Kv7.1
Kv7.1 (KvLQT1) is a potassium channel protein (primary subunit in humans encoded by the KCNQ1 gene). Kv7.1 is a voltage-gated potassium channel present in the cell membranes of cardiac tissue and in inner ear neurons among other tissues. In the cardiac cells, Kv7.1 mediates the IKs (or slow delayed rectifying K+) current that contributes to the repolarization of the cardiac action potential, terminating the cardiac action potential and thereby the heart's contraction.
Mutations in the gene can lead to a defective protein and several forms of inherited arrhythmias as Long QT syndrome which is a prolongation of the QT interval of heart repolarization, short QT syndrome, and familial atrial fibrillation.
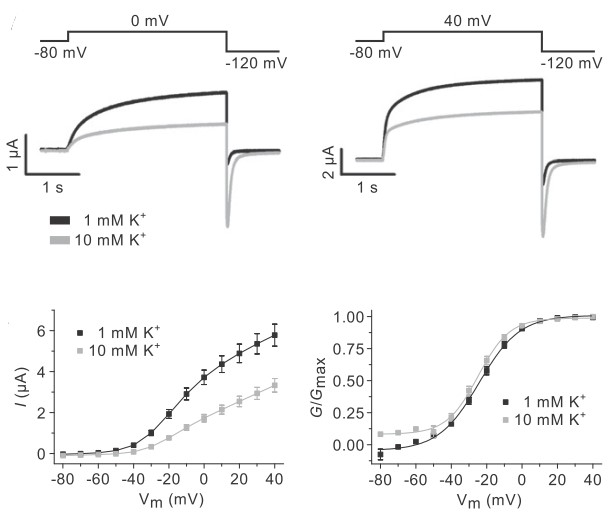
Fig. 1 Kv7.1 current amplitude is reduced by extracellular potassium
In Creative Bioarray, our screening and concentration-response assays (IC50) of compounds for interactions with the KCNQ1/minK channel identify potential risk of QT prolongation in humans, and can be used as a screen in development candidate selection.
Reference
- Larsen AP, et al. Extracellular potassium inhibits Kv7.1 potassium channels by stabilizing an inactivated state. Biophys J. 2011; 101: 818–827.
Related Section
Inquiry

