- Home
-
Screening
- Ionic Screening Service
-
Ionic Screening Panel
- Ligand Gated Ion Channels
- Glycine Receptors
- 5-HT Receptors3
- Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors
- Ionotropic Glutamate-gated Receptors
- GABAa Receptors
- Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulators (CFTR)
- ATP gated P2X Channels
- Voltage-Gated Ion Channels
- Calcium Channels
- Chloride Channels
- Potassium Channels
- Sodium Channels
- ASICs
- TRP Channels
- Other Ion Channels
- Stable Cell Lines
- Cardiology
- Neurology
- Ophthalmology
-
Platform
-
Experiment Systems
- Xenopus Oocyte Screening Model
- Acute Isolated Cardiomyocytes
- Acute Dissociated Neurons
- Primary Cultured Neurons
- Cultured Neuronal Cell Lines
- iPSC-derived Cardiomyocytes/Neurons
- Acute/Cultured Organotypic Brain Slices
- Oxygen Glucose Deprivation Model
- 3D Cell Culture
- iPSC-derived Neurons
- Isolation and culture of neural stem/progenitor cells
- Animal Models
- Techinques
- Resource
- Equipment
-
Experiment Systems
- Order
- Careers
Calcium Transient in Cardiomyocytes
Contractile force is a fundamental physiological parameter of cardiomyocyte function and can be evaluated in heart tissue, isolated papillary muscles, or force-generating engineered heart tissue (EHT). Impairment to this regulatory machinery leads to serious cardiac dysfunctions. As the interdependent regulator between cardiomyocyte electrophysiology and contraction, Ca2+ is important in cardiac functions. Cardiomyocyte contractility is controlled by the excitation-contraction coupling machinery involving Ca2+ influx and efflux within myocytes. Development of contractile force is driven by an increase in cytoplasmic Ca2+ concentration from sarcoplasmic Ca2+ stores.
Creative Bioarray records real-time changes in sarcomere length (Sarcomere shortening) of single isolated cardiomyocytes through video acquisition and monitors Ca2+ cycling in parallel by recording Ca2+ transients from fura-2 loaded isolated cardiomyocytes. Our real-time recording system allows us to investigate into the details of cellular mechanisms of drug-induced negative or positive inotropy.
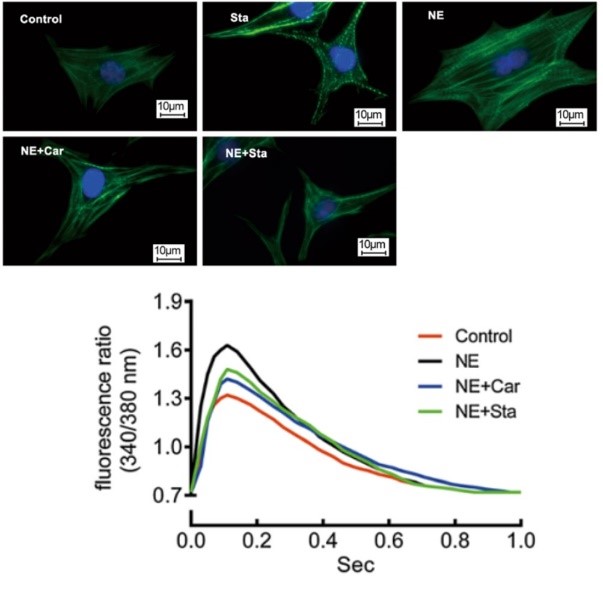
Fig. 1 Representative fluorescent micrographs of cardiomyocytes and calcium transient tracings from cardiac myocytes in NE-treated (NE), NE plus CAR-treated (NE+Car), and NE plus STA-treated (NE+Sta) cells.
To provide cardiac safety assessment, Creative Bioarray cardiac calcium detection service helps our customers monitor spontaneous Ca2+ transients in hiPSC-derived cardiomyocytes in high-throughput way. Using this system, we can record the acute drug effects on cardiomyocytes electrophysiology changes. Our service help accelerating the drug discovery process.
Species & cell types
Human: adult atrial, ventricular, purkinje fibers, iPS-derived ventricular or atrial myocytes
Guinea pig: adult atrial, ventricular, purkinje fibers
Canine: adult atrial, ventricular, purkinje fibers
Rabbits: adult atrial, ventricular, purkinje fibers
Rat: adult atrial, ventricular, purkinje fibers
Creative Bioarray cardiac calcium detection service is based on fluorescence-based assays which measures the intracellular calcium transients. Those compounds that affect ion channels can also affect intracellular calcium transients, this can be indicated by our monitoring system. Our detection is performed on cardiomyocytes cultured in standard 96 or 384 well plates and loaded with a calcium sensitive dye. Compound effects are assessed after the application of single doses and are compared to baseline recording. We also customized the assays to our clients' requirements.
Reference
Zhang C, et al. Effects of stachydrine on norepinephrine-induced neonatal rat cardiac myocytes hypertrophy and intracellular calcium transients. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2014; 14: 474.
Related Section
Inquiry

