- Home
-
Screening
- Ionic Screening Service
-
Ionic Screening Panel
- Ligand Gated Ion Channels
- Glycine Receptors
- 5-HT Receptors3
- Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors
- Ionotropic Glutamate-gated Receptors
- GABAa Receptors
- Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulators (CFTR)
- ATP gated P2X Channels
- Voltage-Gated Ion Channels
- Calcium Channels
- Chloride Channels
- Potassium Channels
- Sodium Channels
- ASICs
- TRP Channels
- Other Ion Channels
- Stable Cell Lines
- Cardiology
- Neurology
- Ophthalmology
-
Platform
-
Experiment Systems
- Xenopus Oocyte Screening Model
- Acute Isolated Cardiomyocytes
- Acute Dissociated Neurons
- Primary Cultured Neurons
- Cultured Neuronal Cell Lines
- iPSC-derived Cardiomyocytes/Neurons
- Acute/Cultured Organotypic Brain Slices
- Oxygen Glucose Deprivation Model
- 3D Cell Culture
- iPSC-derived Neurons
- Isolation and culture of neural stem/progenitor cells
- Animal Models
- Techinques
- Resource
- Equipment
-
Experiment Systems
- Order
- Careers
Psychiatric Model
The total disease burden for neuropsychiatric disorders in the European Union has been recently calculated as 30.1% in women and 23.4% in men. These psychiatric disorders can be categorized into: Schizophrenia, Bipolar disorder, Depression, Anxiety, Psychosis, etc. Animal models have been widely employed for the investigation of the neurobiology of psychiatric disorders and the discovery of new treatments.
Creative Bioarray has a wealth of experience in providing first-class preclinical translational research into the study, treatment and prevention of mental disorders, and we also put efforts in developing precisely tailored research packages to target out client's needs. No matter it is in vitro or in vivo molecular biology techniques, electrophysiological approaches or whole animal behavior studies, our research experts will provide professional consultancy in putting together your study proposal, and also rapidly deliver data of the highest quality to drive forward your research programs.
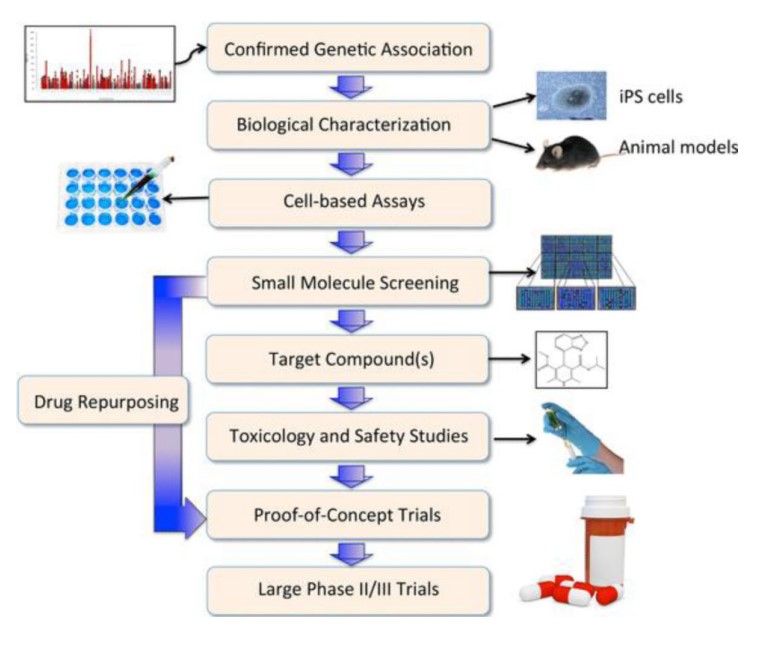
Fig. 1 Illustrative pathway from genetic discovery to novel therapeutics.
Bipolar disorder
Bipolar disorder is a brain disease associated with severe mood swings characterized by mania, depression and in severe cases, psychosis. The treatment to bipolar disorders mainly focuses on symptoms control. In humans, the anti-convulsant drugs valproate and carbamazepine are often used as mood stabilizers for treating acute manic episodes. Besides, lithium is used to treat acute episodes but also to prevent recurrent episodes of illness.
Anxiety
Anxiety is a general term for several disorders that cause nervousness, fear, apprehension and worrying. These disorders affect one's feeling and behaviors manifesting in real physical symptoms. Creative Bioarray conducts contract studies in mice using the marble burying task to assess the efficacy of novel anti-anxiety compounds, such as anxiolytics and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs).
Marble burying test
Marble burying behavior are adopted for evaluation of the level of anxiety in a mouse when it encounters unfamiliar objects. Marbles are placed evenly onto the walls of an empty cage and the mouse is treated with the vehicle or compound before the test (before placed in the cage containing the marbles). The test result is evaluated by the number of marbles discovered (at least 2/3 of area) and the animal behavior by photographing the test cage.
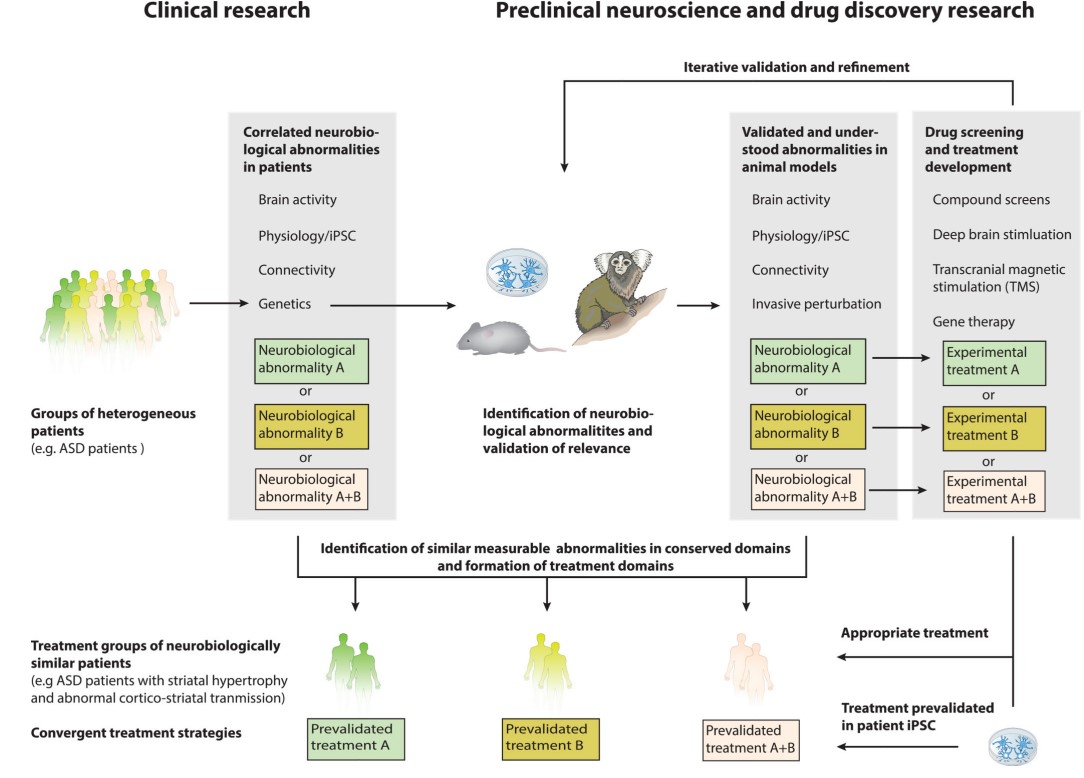
Fig. 2 The path forward: convergence of clinical and preclinical research of neurobiological abnormalities
Chronic social defeat stress
Creative Bioarray uses repeatedly exposing naïve mice to aggressor mice to induce depression for developing chronic social defeat stress paradigm. After 15-d in this emotionally stressful environment, mice display robust depressive phenotypes, which are characteristic of human symptoms. The hallmark behaviors of this model include anhedonia, anxiety and social-avoidance behavior as measured by:
Reduced activity in an open field
Reduced number of rears
Increased immobility
Impaired performance in a long-term memory test (contextual fear conditioning)
Impaired performance in active avoidance test
Collectively, these endpoints provide a comprehensive model of depression to assess the efficacy of your anti-depression therapy candidates. This flexible study paradigm allows either chronic or acute antidepressant treatments, as well as client-specified dosing programs, translating to better predictive value for your drug candidate's intended use.
Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is a chronic, severe, and disabling brain disorder affecting about 1.1% of the U.S. population age 18 and older in any given year. Creative Bioarray has validated a pencyclidine (PCP)-induced deficit model which recapitulates several behavioral deficits, mimicking the symptoms of schizophrenia. This model displays both positive and negative symptoms, including cognitive deficits, and facilitates the development of drugs for either symptom category or in combination. Pre-pulse inhibition of startle is a neurophysiological and behavioral measure of sensorimotor gating. A weaker pre-stimulus (pre-pulse) inhibits the reaction of an animal to a subsequent strong startling stimulus (pulse). Abnormal sensory inhibition may reflect a deficit in processing incoming sensory information. Such deficits are often observed in patients suffering from illnesses like schizophrenia.
Creative Bioarray uses a schizophrenia model of PCP-induced impairment of Pre-pulse Inhibition (PPI) of startle. An antipsychotic drug is typically capable of partly reversing the PPI impairment. The key cognitive tests for efficacy of a substance on negative schizophrenia symptoms are the Morris Water Maze and the Novel Object Recognition test, in which PCP-induced cognitive decline in rats is reversed with an antipsychotic.
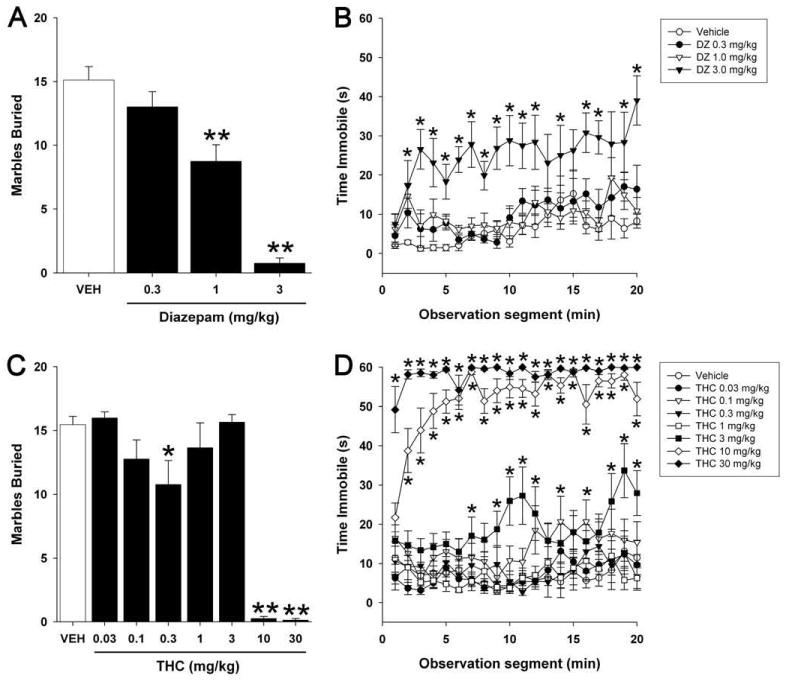
Fig.3 Inhibition of endocannabinoid catabolic enzymes elicits anxiolytic-like effects in the marble burying assay.
Creative Bioarray adopts tests for psychiatric animal models including:
In vivo
Single unit recordings from hippocampus/ striatum/ substantia nigra/ dorsal raphe/ prefrontal cortex/brainstem.
Local field potential/population spike recording from hippocampus: CA1/DG/CA3 by LTP recordings.
MEA test.
In vitro
Whole-cell patch-clamp recordings from brain slices (current/voltage/blind/visualized).
Local field potentials: spontaneous and evoked extracellular recordings from brain slices, including LTP/LTD.
MEA test for Ion channel pharmacology analysis: state-dependency, kinetics, and site of action using cultured and primary dissociated neurons, cell lines.
References
Wittchen HU, et al. The size and burden of mental disorders and other disorders of the brain in Europe 2010. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2011; 21: 655–679.
Kinsey SG, et al. Inhibition of endocannabinoid catabolic enzymes elicits anxiolytic-like effects in the marble burying assay. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2012; 98: 21–27.
Fuentes L, et al. Modeling psychiatric disorders for developing effective treatments. Nat Med. 2016; 93: 292–297.
Jordan S. Psychiatric Genetics and the Future of Personalized Treatment. Depress Anxiety. 2014; 31: 893–898.
Related Section
- Alzheimer's Disease Model
- Parkinson's Disease Model
- Huntington's Disease Model
- Epilepsy Model
- ALS Model
- Autism Spectrum Disorder
- Cerebral-Spinal Injury Model
- Pain Model
- Stroke Model
- Fragile X Model
- Acute/Chronic Heart Failure Model
Inquiry

