- Home
-
Screening
- Ionic Screening Service
-
Ionic Screening Panel
- Ligand Gated Ion Channels
- Glycine Receptors
- 5-HT Receptors3
- Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors
- Ionotropic Glutamate-gated Receptors
- GABAa Receptors
- Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulators (CFTR)
- ATP gated P2X Channels
- Voltage-Gated Ion Channels
- Calcium Channels
- Chloride Channels
- Potassium Channels
- Sodium Channels
- ASICs
- TRP Channels
- Other Ion Channels
- Stable Cell Lines
- Cardiology
- Neurology
- Ophthalmology
-
Platform
-
Experiment Systems
- Xenopus Oocyte Screening Model
- Acute Isolated Cardiomyocytes
- Acute Dissociated Neurons
- Primary Cultured Neurons
- Cultured Neuronal Cell Lines
- iPSC-derived Cardiomyocytes/Neurons
- Acute/Cultured Organotypic Brain Slices
- Oxygen Glucose Deprivation Model
- 3D Cell Culture
- iPSC-derived Neurons
- Isolation and culture of neural stem/progenitor cells
- Animal Models
- Techinques
- Resource
- Equipment
-
Experiment Systems
- Order
- Careers
Huntington's Disease Model
Huntington's disease (HD) is an autosomal dominant neurodegenerative genetic disorder affects muscle coordination leading to cognitive decline and psychiatric manifestations. HD patients exhibit a diverse set of symptoms with well-recognized emotional, cognitive and motor components. It typically becomes noticeable at middle age. Although onset is generally within the fourth or fifth decade, the disease can start at any time from early childhood until very old age with a mean duration of 15-20 years. Symptoms of the disease may be different between individuals and among affected members of the same family, but the progress is predictable for most individuals. As the disease advances, patients show uncoordinated, jerky body movements, decline in mental abilities, along with behavioral (physical abilities are gradually impeded until coordinated movement becomes very difficult) and psychiatric problems (mental abilities generally decline into dementia).
HD is mainly caused by the mutation which is an unstable expansion of CAG repeats in the huntingtin gene. The disease is caused by an autosomal dominant mutation of the huntingtin gene (CAG^polyglutamine repeat expansion. Creative Bioarray has phenotypically characterized extensively both transgenic and knock-in models of the disease.
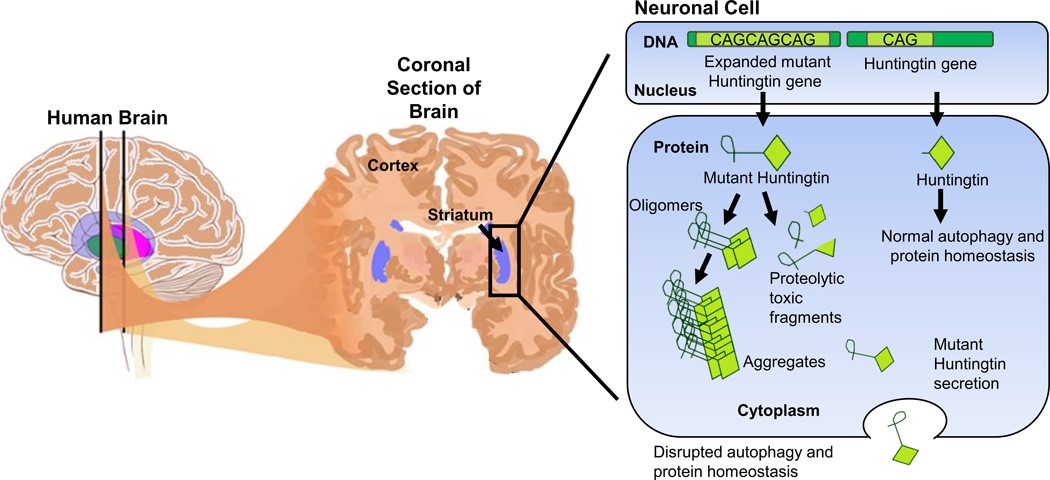
Fig.1 A schematic representation of the brain highlighting the striatum and the pathology of HD in a neuronal cell
Two HD animal models are available in Creative Bioarray. The R6/2 transgenic mouse model was the first developed and widely used to understand the pathogenesis of the disease as well as for the evaluation of new therapies. These mice carrying around 120 CAG repeats present severe weight loss, progressive motor, cognitive and psychiatric deficits, and a reduced life expectancy (18-20 weeks). The Q175 Knock-in model derived from a spontaneous expansion from Q140 Knock-in colony, display also a slower progressive motor and cognitive phenotype than the R6/2 model.
Creative Bioarray provides the R6/2 mice model of human Huntington's disease (HD) by expressing a portion of the human HD gene under human gene promoter elements (1 kb of 5 UTR sequence and exon 1 together with ~140 CAG repeats). Expression of this amino-terminal fragment of the huntingtin protein with its polyglutamine expansion is sufficient to reproduce the phenotype of human HD. Both the R6/2 and Q175 mouse models are kept in Creative Bioarray.
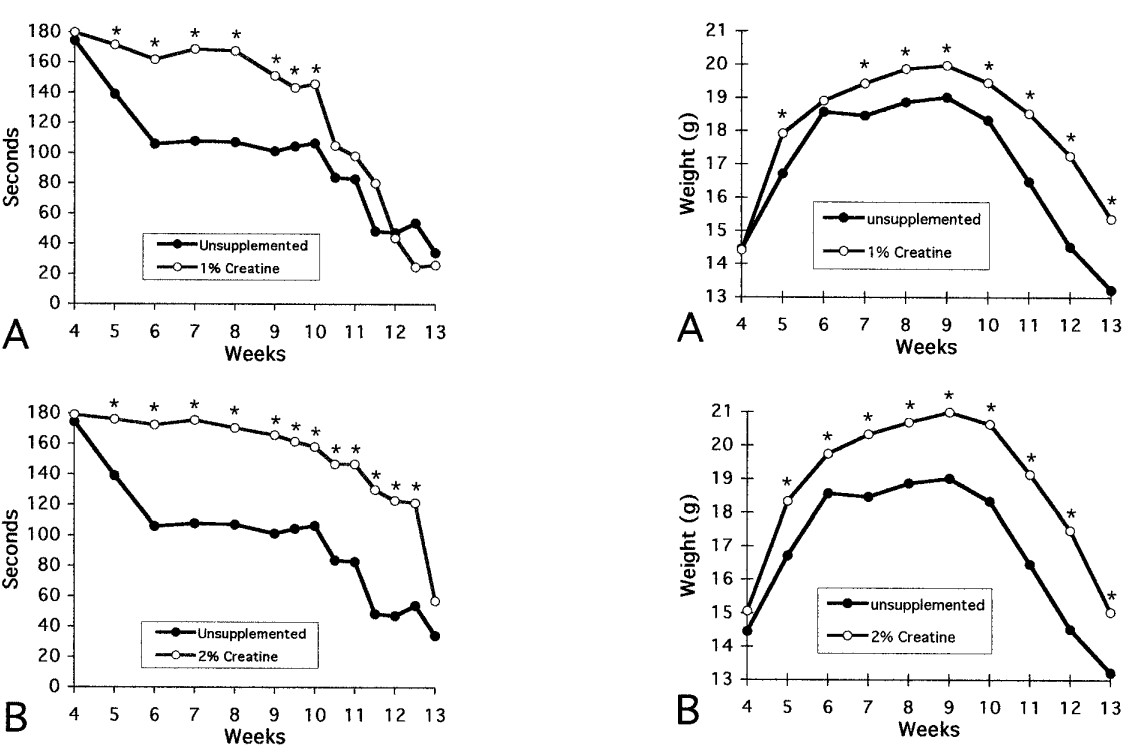
Fig.2 Effects of 1, 2, and 3% creatine on rotarod performance and on body weight in R6/2 HD transgenic mice
Tests
General test
Body weight
Motor functionanalysis
Open field test
Rotarod test
Grip strength test
Rear climbing test
Cognitive deficits
Two-choice swim test
Contextual fear conditioning
Neurological index
In vivo brain imaging
MRI for brain volumetry (whole brain, cortex, striatum)
MRS for striatal metabolites
We also provide immunohistochemistry tests, inflammatory markers staining, iron accumulation and dopaminergic neuro-transmission tests for HD animal model study. To accelerating the identification of treatments for HD, Creative Bioarray has developed customized animal model service in HD research.
References
Ferrante R, et al. Neuroprotective effects of creatine in a transgenic mouse model of Huntington's disease. J Neurosci. 2000; 20: 4389–4397.
Zhang N, et al. iPSC-based drug screening for Huntingtons disease. Brain Res. 2016; 1638: 42–56.
Related Section
- Alzheimer's Disease Model
- Parkinson's Disease Model
- Epilepsy Model
- ALS Model
- Psychiatric Model
- Autism Spectrum Disorder
- Cerebral-Spinal Injury Model
- Pain Model
- Stroke Model
- Fragile X Model
- Acute/Chronic Heart Failure Model
Inquiry

