- Home
-
Screening
- Ionic Screening Service
-
Ionic Screening Panel
- Ligand Gated Ion Channels
- Glycine Receptors
- 5-HT Receptors3
- Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors
- Ionotropic Glutamate-gated Receptors
- GABAa Receptors
- Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulators (CFTR)
- ATP gated P2X Channels
- Voltage-Gated Ion Channels
- Calcium Channels
- Chloride Channels
- Potassium Channels
- Sodium Channels
- ASICs
- TRP Channels
- Other Ion Channels
- Stable Cell Lines
- Cardiology
- Neurology
- Ophthalmology
-
Platform
-
Experiment Systems
- Xenopus Oocyte Screening Model
- Acute Isolated Cardiomyocytes
- Acute Dissociated Neurons
- Primary Cultured Neurons
- Cultured Neuronal Cell Lines
- iPSC-derived Cardiomyocytes/Neurons
- Acute/Cultured Organotypic Brain Slices
- Oxygen Glucose Deprivation Model
- 3D Cell Culture
- iPSC-derived Neurons
- Isolation and culture of neural stem/progenitor cells
- Animal Models
- Techinques
- Resource
- Equipment
-
Experiment Systems
- Order
- Careers
Stroke Model
Stroke is one of the most frequent causes of death and adult disability. There are two main types of stroke: ischemic and hemorrhagic. Ischemic stroke (caused by lack of blood flow) accounts for about 80~90% of the incidence of stroke. Signs and symptoms of a stroke may include:
Trouble with speaking and understanding
Trouble with walking
Trouble with seeing in one or both eyes
Paralysis or numbness of the face, arm or leg
Headache
Since 1995, recombinant tissue plasminogen activator (rtPA) has been used as a thrombolytic agent to dissolve blood clots that occlude cerebral arteries, leading to reperfusion of the ischemic brain. However, eligibility for thrombolysis currently stands at approximately 15%, largely due to a lack of efficacy beyond 4.5-h post-stroke, as well as the risk of hemorrhagic transformation. Other therapies, such as anti-platelet drugs, can be used to prevent further coagulation, but there remains a dearth of novel therapeutic agents.
There are currently a large number of well-characterized, ischemic stroke animal models available for pre-clinical research. For stroke studies, Creative Bioarray provides studies for neuroprotection and reduction of infarct, as well as longer-term, more comprehensive studies looking at functional and cognitive outcomes or stroke prevention. In Creative Bioarray, all studies can be customized and adjusted to meet client needs.
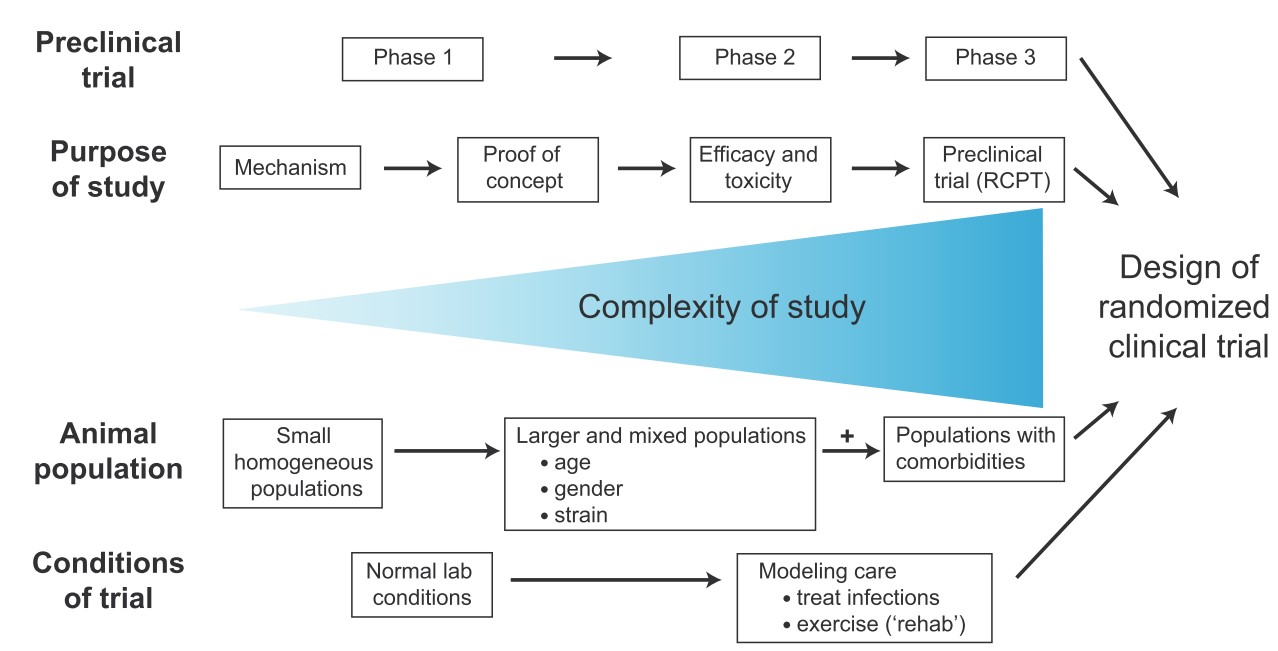
Fig. 1 The preclinical trial phases of translational stroke research
Animal models of stroke and ischemia available for use in our studies include:
Focal Ischemia Models
Transient middle cerebral artery occlusion (tMCAO)
Permanent middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO)
Thromboembolic MCA occlusion: Endothelin-1-induced middle cerebral artery occlusion (EMCAO); Photo-thrombosis model
Global brain ischemia
Four vessel occlusion (4VO)
Two vessel occlusion (2VO)
Cardiac arrest and resuscitation
Other ischemia models
Hind limb ischemia peripheral model
Stroke prevention model in Dahl/Salt Sensitive (Dahl/SS) or Stroke-Prone Spontaneously Hypertensive (SHRSP) rats
Cerebral stroke models can be established by the latest micro-neurosurgery techniques. In Creative Bioarray, we adopt micro-catheter embolization or blood vessel clamping method through-pterion, orbital or supraorbital operation to build the cerebral stroke model. The comprehensive testing package can be provided including:
A standard neurological deficit score: sensory system defects, conscious state, motor system, skeletal muscle coordination
MRI imaging for judging the state and calculating the relative infarct volume percentage: Both conventional MRI and MRI diffusion weighted imaging (imaging diffusion-weighted, DWI) are available
Physiological parameters: BP, BBT, pH, pCO2, pO2, sO2, and GLU
Since the focal cerebral ischemic model of stroke is commonly used to evaluate ischemic injury of the brain. Here, we give an example of middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) model. The middle cerebral artery is one common focus of human ischemic stroke, so it is widely believed that is a standard animal model of focal cerebral ischemia. MCAO is generally achieved mechanically and may be either transient with variable duration or permanent. The occlusion of the middle cerebral artery can result in following defects: sensory loss of the contralateral face and arm, contralateral neglect syndrome (usually caused by damage to the right hemisphere), aphasia (usually caused by damage to the left hemisphere), paralysis (-plegia) or weakness (-paresis) of the contralateral face and arm, etc.
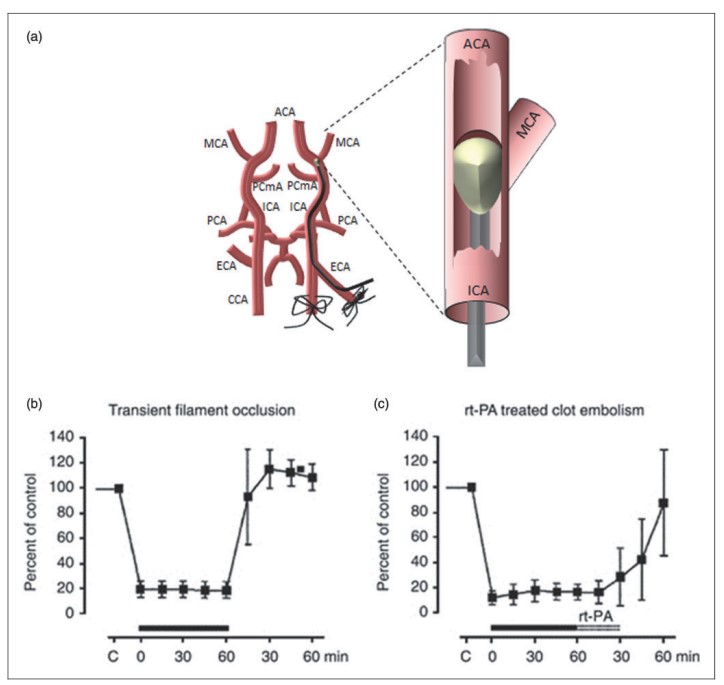
Fig.2 Illustration of the tMCAO model in rodents
There are several kinds of methods in building MCAO models, such as vessel pressure, operation through orbit, brain vessel embolism, vessel line-occluding, photochemistry method, and craniotomy. We are capable of using micro-neurosurgery technique to build MCAO models. We provide optional micro-catheter embolization or blood vessel clamping method through-pterion, orbital or supraorbital operation.
Creative Bioarray is a senior expert in the field of rodent and Non-Human Primate model's establishment. Creative Bioarray offers guaranteed MCAO modeling service based on our advanced technology platform and extensive expertise. We are glad to offer one-stop, custom-oriented service package from initial model establishment to final data analysis.
References
Mergenthaler P, Meisel A. Do stroke models model stroke? Dis Model Mech.2012; 5: 718–725.
Sutherland BA, et al. The transient intraluminal filament middle cerebral artery occlusion model as a model of endovascular thrombectomy in stroke. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2016; 36: 363–369.
Related Section
- Alzheimer's Disease Model
- Parkinson's Disease Model
- Huntington's Disease Model
- Epilepsy Model
- ALS Model
- Psychiatric Model
- Autism Spectrum Disorder
- Cerebral-Spinal Injury Model
- Pain Model
- Fragile X Model
- Acute/Chronic Heart Failure Model
Inquiry

