- Home
-
Screening
- Ionic Screening Service
-
Ionic Screening Panel
- Ligand Gated Ion Channels
- Glycine Receptors
- 5-HT Receptors3
- Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors
- Ionotropic Glutamate-gated Receptors
- GABAa Receptors
- Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulators (CFTR)
- ATP gated P2X Channels
- Voltage-Gated Ion Channels
- Calcium Channels
- Chloride Channels
- Potassium Channels
- Sodium Channels
- ASICs
- TRP Channels
- Other Ion Channels
- Stable Cell Lines
- Cardiology
- Neurology
- Ophthalmology
-
Platform
-
Experiment Systems
- Xenopus Oocyte Screening Model
- Acute Isolated Cardiomyocytes
- Acute Dissociated Neurons
- Primary Cultured Neurons
- Cultured Neuronal Cell Lines
- iPSC-derived Cardiomyocytes/Neurons
- Acute/Cultured Organotypic Brain Slices
- Oxygen Glucose Deprivation Model
- 3D Cell Culture
- iPSC-derived Neurons
- Isolation and culture of neural stem/progenitor cells
- Animal Models
- Techinques
- Resource
- Equipment
-
Experiment Systems
- Order
- Careers
Assays for Neuropsychiatric Disorders
Neurocognitive dysfunction is a core feature of several psychiatric disorders, including schizophrenia and bipolar illness however, the severity and pattern of cognitive impairment in these two disorders differs significantly, as does the timing of the onset of cognitive deficits. Compelling clinical, social, and economic reasons exist to innovate in the process of drug discovery for neuropsychiatric disorders.
Early stage drug discovery for neuropsychiatric disorders, includes support of quantitative biochemistry, functional genomics, proteomics, and perhaps most notably, high-throughput and high-content chemical screening. Animal behavior tests for treating neuropsychiatric disorders are required at a later stage. To accelerate development of compounds to treat schizophrenia and related disorders, Creative Bioarray offers a variety of assays, including a number of well-established ones related to dopaminergic or hypo-glutamatergic hyperactivity.
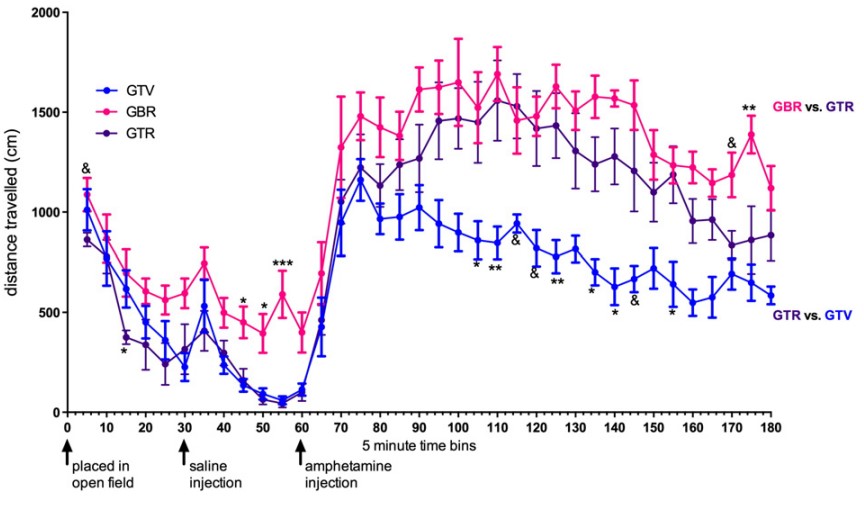
Fig.1 The effect of raloxifene on amphetamine-induced locomotion in rats with or without exogenous circulating testosterone
Compounds can also be assessed in the conditioned avoidance assay, as selective disruption of the conditioned response is a characteristic property of both typical and novel antipsychotic agents. As with all of our services, Creative Bioarray works to design a program that is specific to your objectives.
Assays
Amphetamine/PCP induced locomotor activity
Apomorphine induced rearing climbing
Conditioned Avoidance Response
Reference
Purves-Tyson TD, et al. Testosterone attenuates and the selective estrogen receptor modulator, raloxifene, potentiates amphetamine-induced locomotion in male rats. Horm Behav 2015; 70: 73–84.
Related Section
- Anxiety-Depression and Social Interaction Evaluation
- Spontaneous Locomotor Functions
- Cognitive Functions
Inquiry

