- Home
-
Screening
- Ionic Screening Service
-
Ionic Screening Panel
- Ligand Gated Ion Channels
- Glycine Receptors
- 5-HT Receptors3
- Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors
- Ionotropic Glutamate-gated Receptors
- GABAa Receptors
- Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulators (CFTR)
- ATP gated P2X Channels
- Voltage-Gated Ion Channels
- Calcium Channels
- Chloride Channels
- Potassium Channels
- Sodium Channels
- ASICs
- TRP Channels
- Other Ion Channels
- Stable Cell Lines
- Cardiology
- Neurology
- Ophthalmology
-
Platform
-
Experiment Systems
- Xenopus Oocyte Screening Model
- Acute Isolated Cardiomyocytes
- Acute Dissociated Neurons
- Primary Cultured Neurons
- Cultured Neuronal Cell Lines
- iPSC-derived Cardiomyocytes/Neurons
- Acute/Cultured Organotypic Brain Slices
- Oxygen Glucose Deprivation Model
- 3D Cell Culture
- iPSC-derived Neurons
- Isolation and culture of neural stem/progenitor cells
- Animal Models
- Techinques
- Resource
- Equipment
-
Experiment Systems
- Order
- Careers
Kv1.5
Atrial fibrillation is a rhythm disorder characterized by chaotic electrical activity of cardiac atria. Predisposing to stroke and heart failure, this common condition is increasingly recognized as a heritable disorder. Genomic DNA scanning revealed a nonsense mutation in KCNA5 that encodes Kv1.5, a voltage-gated potassium channel expressed in human atria. Mutations in this gene have been related to both atrial fibrillation and sudden cardiac death.
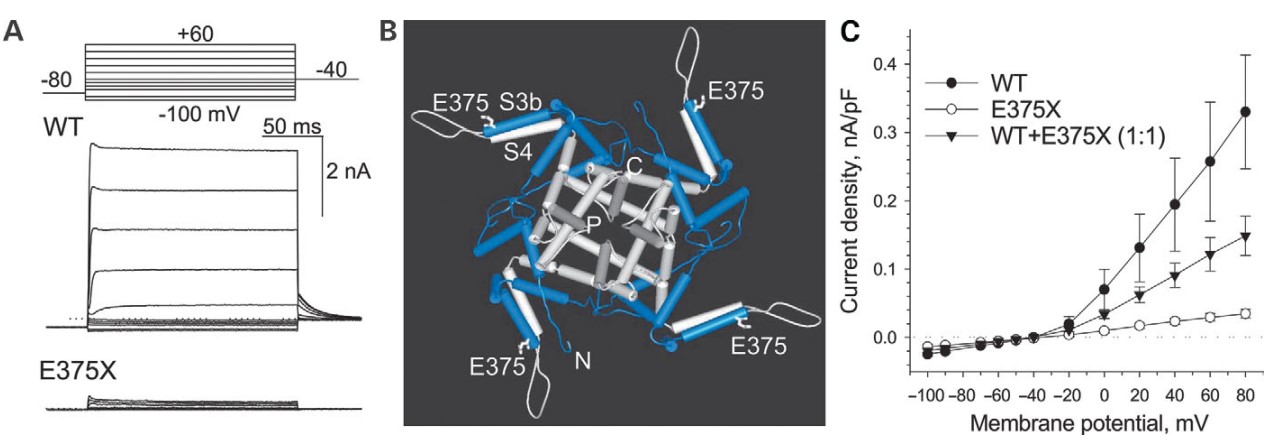
Fig. 1 Loss-of-function E375X mutation exerts a dominant-negative effect on Kv1.5 function
Staffed with a group of experts that have gained years of experience in ion channel safety assays and cardiotoxicity assessment, Creative Bioarray offers screening analysis and concentration-response assays (IC50) of compounds inhibit Kv1.5 to evaluate compound cardiovascular safety and this service can be used as a screen in development candidate selection.
Reference
- Olson TM, et al. Kv1.5 channelopathy due to KCNA5 loss-of-function mutation causes human atrial fibrillation. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2006; 15: 2185–2191.
Related Section
Inquiry

