- Home
-
Screening
- Ionic Screening Service
-
Ionic Screening Panel
- Ligand Gated Ion Channels
- Glycine Receptors
- 5-HT Receptors3
- Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors
- Ionotropic Glutamate-gated Receptors
- GABAa Receptors
- Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulators (CFTR)
- ATP gated P2X Channels
- Voltage-Gated Ion Channels
- Calcium Channels
- Chloride Channels
- Potassium Channels
- Sodium Channels
- ASICs
- TRP Channels
- Other Ion Channels
- Stable Cell Lines
- Cardiology
- Neurology
- Ophthalmology
-
Platform
-
Experiment Systems
- Xenopus Oocyte Screening Model
- Acute Isolated Cardiomyocytes
- Acute Dissociated Neurons
- Primary Cultured Neurons
- Cultured Neuronal Cell Lines
- iPSC-derived Cardiomyocytes/Neurons
- Acute/Cultured Organotypic Brain Slices
- Oxygen Glucose Deprivation Model
- 3D Cell Culture
- iPSC-derived Neurons
- Isolation and culture of neural stem/progenitor cells
- Animal Models
- Techinques
- Resource
- Equipment
-
Experiment Systems
- Order
- Careers
Fragile X Model
Fragile X syndrome (FXS) is the most common inherited form of autism and intellectual disability and caused by silencing of a single gene: fragile X mental retardation 1 (Fmr1). The FMR1 mutation underlying the FXS is the most frequent cause of inherited mental retardation and is interesting here because about 10–30% of these patients are also diagnosed with autism Clinical evidence demonstrates clear abnormalities in sensory processing and communication in humans with FXS.
Creative Bioarray provides Fmr1 KO mice which contains a deletion of the Fmr1 for Fragile X syndrome study. Mutations in Fmr1 result in FXS, the leading monogenic cause of autism, making this rat useful for the study of both FXS and autism.
Primates have been used to study social relations and social communication, but they have limitations because of their high financial cost, long developmental time span, the fact that genetic manipulation is impractical, and ethical considerations. Rodents do not suffer from these drawbacks. The Fmr1 KO mouse is a valid model of the FXS and many research data on behavioral and sensory-motor characteristics of this model have been gathered. Consistent with the clinical characteristics, the Fmr1 KO mouse model exhibits a variety of abnormal responses to auditory stimuli, and therefore provides a means of studying the mechanisms and potential drug therapies for FXS.
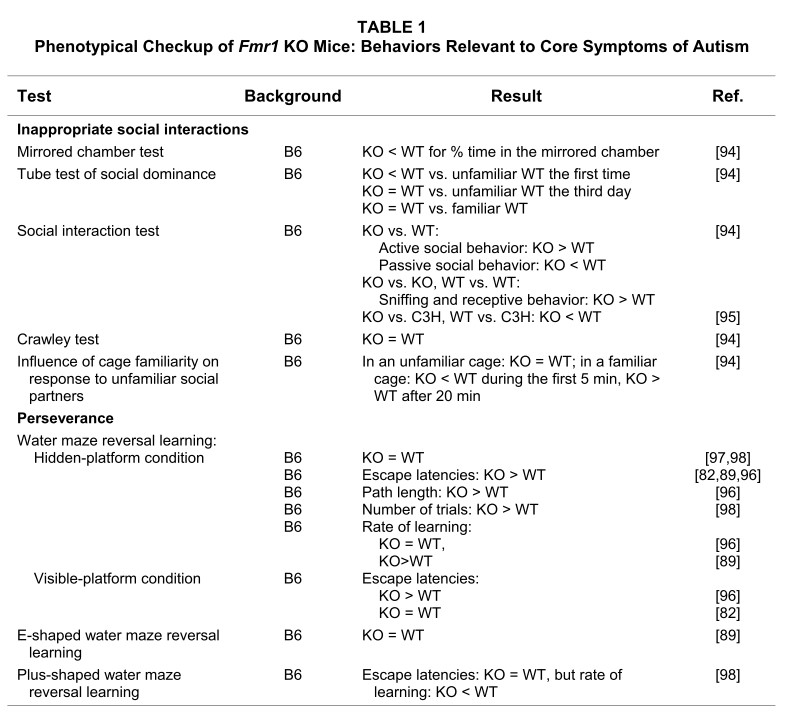
Audiogenic seizures is one of the well-known and commonly used phenotypes in pre-clinical studies of FXS with Fmr1 KO mice. Abnormal auditory evoked responses have been used as outcome measures to test therapeutics in both FXS patients and also Fmr1 KO mice. Creative Bioarray breeds the mice and routinely screens novel therapies for attenuation of audiogenic seizures in 21-d old Fmr1 KO mice.
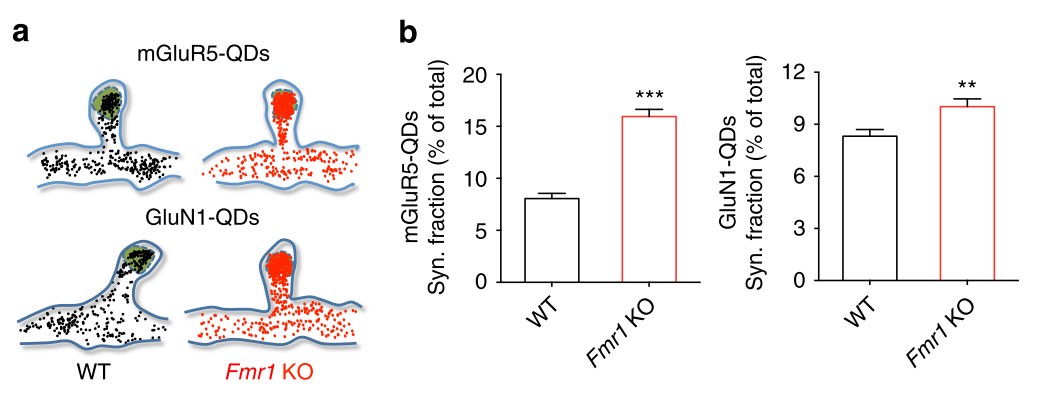
Fig. 1 mGluR5 and GluN1 are more confined within the synaptic compartment in Fmr1 KO neurons.
References
Aloisi E, et al. Altered surface mGluR5 dynamics provoke synaptic NMDAR dysfunction and cognitive defects in Fmr1 knockout mice. Nat Commun. 2017; 8: 1103.
Bernardet M, Crusio WE. Fmr1 KO mice as a possible model of autistic features. The Scientific World Journal. 2006; 6: 1164–1176.
Related Section
- Alzheimer's Disease Model
- Parkinson's Disease Model
- Huntington's Disease Model
- Epilepsy Model
- ALS Model
- Psychiatric Model
- Autism Spectrum Disorder
- Cerebral-Spinal Injury Model
- Pain Model
- Stroke Model
- Acute/Chronic Heart Failure Model
Inquiry

