- Home
-
Screening
- Ionic Screening Service
-
Ionic Screening Panel
- Ligand Gated Ion Channels
- Glycine Receptors
- 5-HT Receptors3
- Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors
- Ionotropic Glutamate-gated Receptors
- GABAa Receptors
- Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulators (CFTR)
- ATP gated P2X Channels
- Voltage-Gated Ion Channels
- Calcium Channels
- Chloride Channels
- Potassium Channels
- Sodium Channels
- ASICs
- TRP Channels
- Other Ion Channels
- Stable Cell Lines
- Cardiology
- Neurology
- Ophthalmology
-
Platform
-
Experiment Systems
- Xenopus Oocyte Screening Model
- Acute Isolated Cardiomyocytes
- Acute Dissociated Neurons
- Primary Cultured Neurons
- Cultured Neuronal Cell Lines
- iPSC-derived Cardiomyocytes/Neurons
- Acute/Cultured Organotypic Brain Slices
- Oxygen Glucose Deprivation Model
- 3D Cell Culture
- iPSC-derived Neurons
- Isolation and culture of neural stem/progenitor cells
- Animal Models
- Techinques
- Resource
- Equipment
-
Experiment Systems
- Order
- Careers
Acute Dissociated Neurons
Neurons are the electrically excitable cells in the central and peripheral nervous systems (CNS and PNS), which include the brain, spinal cord, peripheral ganglia, and sensory organs. Information is processed in a single neuron (the soma, dendrite, and axon) by electrical signals and is subsequently transmitted to other cells through synapses. Examining neuronal ion channels and action potentials is important for understanding the electrophysiological and pathophysiological functions of the CNS and PNS.
Although established neuronal cell lines (such as human and animal neuroblastomas) may provide valuable information, the extrapolation of such results to primary neuronal cells remains important. The endless debate focuses on whether such transformed cells reflect the genetic, biochemical, and physiological aspects of primary neuronal cells. Therefore, a technique for isolating primary CNS and PNS neurons from adult animals is advantageous for studying the physiological and biochemical neuronal functions. Access to a viable cell is critical for the patch-clamp experiments.
Combined with other techniques including patch-clamp, single-cell real-time PCR, immunocytochemistry, and gene transfection, Creative Bioarray can help you use successfully isolated primary neurons from young and adult animals to investigate the physiological and biochemical functions of the brain in health and disease.
Isolated primary neurons have several advantages for electrophysiological and biochemical studies.
Isolating the primary neurons removes the complicated biophysical and biochemical interactions with neighboring cells, which allows for measurement of the direct effect of the compound treatment on these neurons and avoids the ambiguity of interpreting the cellular target of the treatment compound.
Isolated primary neurons offer the ability to explore the molecular and cellular mechanisms associated with the cell excitability and the release of transmitters or modulators.
Using primary neurons, it is easy to precisely change the experimental environment affecting neurons, which is essential for investigating the electrophysiological properties of these cells.
In long-term culture of isolated primary neurons, time-dependent alteration of morphological characteristics (such as neuritogenesis, connectivity, and toxicity) can be continuously investigated.
Isolated PNS and CNS neurons are both available in Creative Bioarray:
Isolation of PNS Neurons
Electrophysiological studies were performed on acutely isolated PNS neurons from adult tissue preparations. Although there are differences in neuronal isolation from ganglia and sensory organs, mechanical and enzymatic dissociation of the neurons is the common, fundamental procedure for the various ganglia and sensory organs.
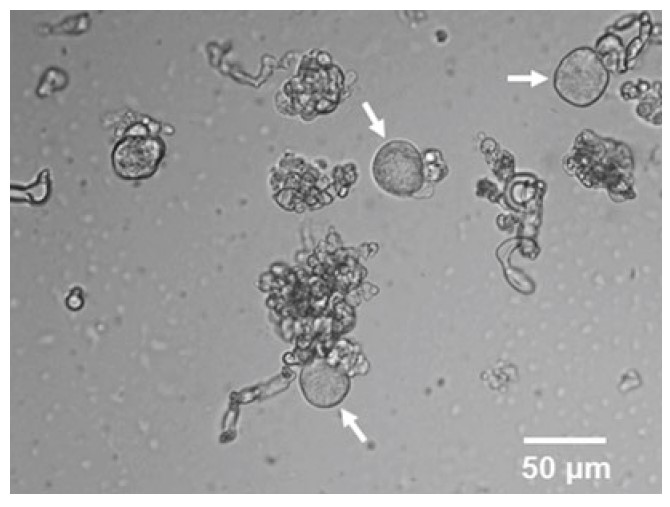
Fig. 1 Primary nodose neurons acutely isolated from adult rats. Arrows indicate the spherical neurons with distinct edges and smooth surface
Isolation of CNS Neurons
Neurons from embryonic and neonatal brains are isolated for electrophysiological studies. A critical question is whether the electrophysiological characteristics of these CNS neurons are similar to those present in adult animals. This is especially true for animal models with adult onset or induction of disease (e.g., diabetes, hypertension, and chronic heart failure). Creative Bioarray has the ability to successfully isolate neurons from adult brain can aid in investigating CNS neuron functions in physiological and pathophysiological conditions.
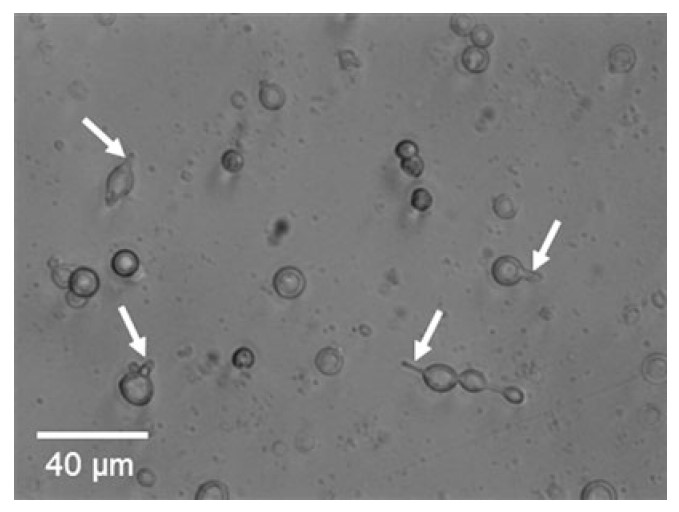
Fig.2 Photomicrograph of acutely isolated rat hypothalamic neurons after 3-h in culture. Arrows indicate small process of the hypothalamic neurons
Furthermore, acute isolation technique can aid in the investigation of the effects of neurotransmitters, neuromodulators, and pharmacological compounds on neurons in the physiological and pathophysiological states. Creative Bioarray also adjusts the procedure for better in isolation of primary neurons from different ganglia or different brain regions according to your project.
Reference
Xiong, Huangui, and Howard E. Gendelman (eds). Current laboratory methods in neuroscience research. Springer, 2014.
Related Section
- Xenopus Oocyte Screening Model
- Acute Isolated Cardiomyocytes
- Primary Cultured Neurons
- Cultured Neuronal Cell Lines
- iPSC-derived Cardiomyocytes/Neurons
- Acute/Cultured Organotypic Brain Slices
- Oxygen Glucose Deprivation Model
- 3D Cell Culture
- iPSC-derived Neurons
- Isolation and culture of neural stem/progenitor cells
Inquiry

