- Home
-
Screening
- Ionic Screening Service
-
Ionic Screening Panel
- Ligand Gated Ion Channels
- Glycine Receptors
- 5-HT Receptors3
- Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors
- Ionotropic Glutamate-gated Receptors
- GABAa Receptors
- Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulators (CFTR)
- ATP gated P2X Channels
- Voltage-Gated Ion Channels
- Calcium Channels
- Chloride Channels
- Potassium Channels
- Sodium Channels
- ASICs
- TRP Channels
- Other Ion Channels
- Stable Cell Lines
- Cardiology
- Neurology
- Ophthalmology
-
Platform
-
Experiment Systems
- Xenopus Oocyte Screening Model
- Acute Isolated Cardiomyocytes
- Acute Dissociated Neurons
- Primary Cultured Neurons
- Cultured Neuronal Cell Lines
- iPSC-derived Cardiomyocytes/Neurons
- Acute/Cultured Organotypic Brain Slices
- Oxygen Glucose Deprivation Model
- 3D Cell Culture
- iPSC-derived Neurons
- Isolation and culture of neural stem/progenitor cells
- Animal Models
- Techinques
- Resource
- Equipment
-
Experiment Systems
- Order
- Careers
Sodium Channels
Sodium channels are that form ion channels, conducting sodium ions (Na+) through cellular plasma membrane. Voltage-gated sodium channels (also called "VGSCs" or "Nav channel") are present in the membrane of most excitable cells and are involved in many cardiac or neuronal diseases.
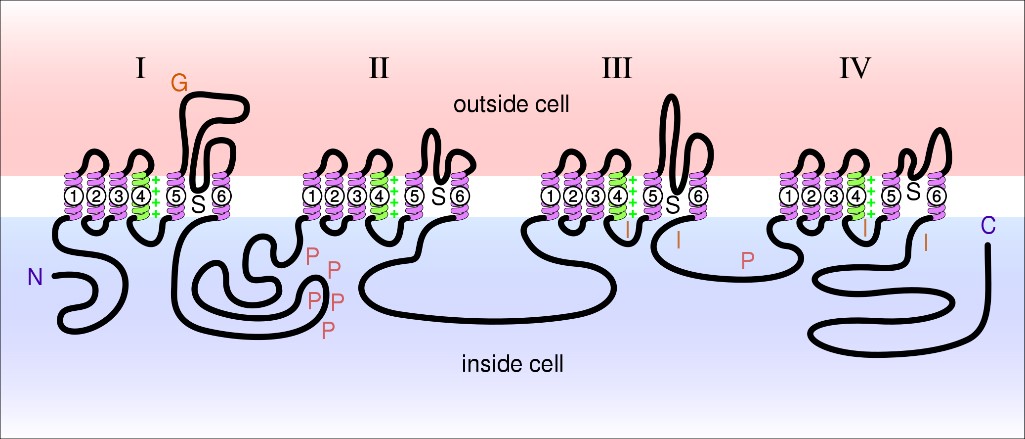
Fig.1 Sodium channels α-subunit
Sodium channels are the main component and responsible for the rising phase of action potentials in excitable cells such as neurons, myocytes, and some certain types of glia. The dynamics of sodium channels can be classified into three different states: resting, active and inactive states.
Functions
Mediating the sodium ion permeability of excitable membranes in a voltage-dependent form.
Forming a sodium-selective channel through which Na+ ions may pass in accordance with their electrochemical gradient.
Assuming opened or closed conformations in response to the voltage difference across the membrane.
Plays a key role in brain, probably by regulating the moment when neurotransmitters are released in neurons.
Involved in sensory perception of mechanical pain: activation in somatosensory neurons induces pain without neurogenic inflammation and produces hypersensitivity to mechanical, but not thermal stimuli.
Genetic mutations that cause persistent activity in sodium channels can cause disease by creating excessive activity of certain kinds of neurons. Mutations that interfere with Na+ channel inactivation can contribute to cardiovascular diseases or epileptic seizures by window currents, which can cause muscle and/or nerve cells to become over-excited.
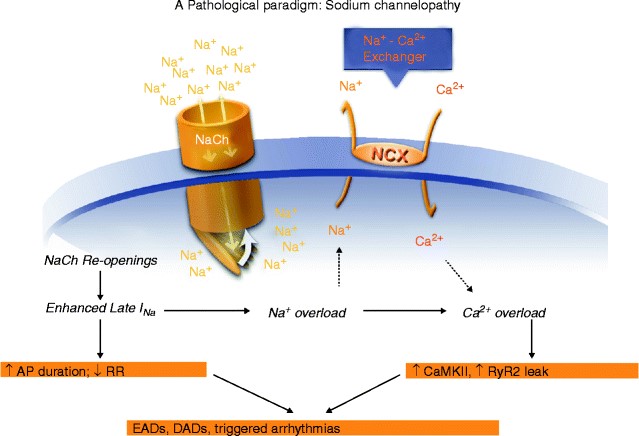
Fig. 2 Pathological consequences of acquired and/or inherited Na+ channelopathies
The specific tissue localizations of sodium channels
Central nervous system, peripheral neurons and dorsal root ganglia
9 known members: Nav1.1- Nav1.9Cardiac myocytes
Nav1.5Skeletal muscle
Nav1.4
Here in Creative Bioarray, we provide target screening on a series of sodium channels listed as below:
Nav1.1 (SCN1A)
Disease: mutations in SCN1A are responsible for many types of epilepsies (generalized epilepsy with febrile seizures, severe myoclonic epilepsy in infancy) and some forms of familial hemiplegic migraine.
Therapeutic Targets: seizure, stroke and pain.
Nav1.2 (SCN2A)
Disease: mutations are associated with benign familial neonatal-infantile seizures.
Therapeutic Targets: seizure, stroke and pain.
Nav1.3 (SCN3A)
Disease: upregulated in nerve injury.
Therapeutic Targets: seizure and pain.
Nav1.5 (SCN5A)
Tissue-specific Location: heart and upregulated in breast cancer cells.
Disease: mutations in SCN5A are responsible for some forms of long QT and short QT syndromes, progressive cardiac conduction defect, sick sinus node syndrome, and dilated cardiomyopathy, Brugada syndrome (BrS), congenital heart block.
Therapeutic Target: anti-targets in cardiac risk assessment.
Nav1.6 (SCN8A)
Tissue-specific Location: central and peripheral nervous systems.
Disease: Mutations in the mouse ortholog cause ataxia and other movement disorders.
Therapeutic Target: multiple sclerosis and seizure.
Nav1.7 (SCN9A)
Disease: mutations in this channel are associated with primary erythromelalgia, insensitivity to pain and paroxysmal extreme pain disorder.
Therapeutic Target: pain treatment and nociceptive disorders.
Nav1.8 (SCN10A)
Disease: upregulated in chronic/inflammatory pain.
Therapeutic Target: pain treatment.
Related Products
- Overexpression Cell Line
| Catalog | Product Name | Gene Name | Species | Morphology | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACC-RI0047 | Human SCN1A Stable Cell Line-HEK293 | SCN1A | Human | Epithelial | INQUIRY |
| ACC-RI0048 | Human SCN2A Stable Cell Line-CHO | SCN2A | Human | Epithelial-like | INQUIRY |
| ACC-RI0049 | Human SCN3A Stable Cell Line-CHO | SCN3A | Human | Epithelial-like | INQUIRY |
| ACC-RI0050 | Human SCN4A Stable Cell Line-HEK293 | SCN4A | Human | Epithelial | INQUIRY |
| ACC-RI0051 | Human SCN5A Stable Cell Line-HEK293 | SCN5A | Human | Epithelial | INQUIRY |
| ACC-RI0052 | Human SCN8A Stable Cell Line-HEK293 | SCN8A | Human | Epithelial | INQUIRY |
| ACC-RI0053 | Human SCN9A Stable Cell Line-HEK293 | SCN9A | Human | Epithelial | INQUIRY |
| ACC-RI0054 | Human SCN10A Stable Cell Line-HEK293 | SCN10A | Human | Epithelial | INQUIRY |
| ACC-RI0055 | Rat Nav1.8 Stable Cell Line-ND7-23 | Nav1.8 | Rat | Neuronal | INQUIRY |
| ACC-RI0154 | Human SCN1A Stable Cell Line-CHO | SCN1A | Human | Epithelial-like | INQUIRY |
Related Section
- Ligand Gated Ion Channels
- Glycine Receptors
- 5-HT Receptors3
- Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors
- Ionotropic Glutamate-gated Receptors
- GABAa Receptors
- Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulators (CFTR)
- ATP gated P2X Channels
- Voltage-Gated Ion Channels
- Calcium Channels
- Chloride Channels
- Potassium Channels
- ASICs
- TRP Channels
- Other Ion Channels
Inquiry

