- Home
-
Screening
- Ionic Screening Service
-
Ionic Screening Panel
- Ligand Gated Ion Channels
- Glycine Receptors
- 5-HT Receptors3
- Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors
- Ionotropic Glutamate-gated Receptors
- GABAa Receptors
- Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulators (CFTR)
- ATP gated P2X Channels
- Voltage-Gated Ion Channels
- Calcium Channels
- Chloride Channels
- Potassium Channels
- Sodium Channels
- ASICs
- TRP Channels
- Other Ion Channels
- Stable Cell Lines
- Cardiology
- Neurology
- Ophthalmology
-
Platform
-
Experiment Systems
- Xenopus Oocyte Screening Model
- Acute Isolated Cardiomyocytes
- Acute Dissociated Neurons
- Primary Cultured Neurons
- Cultured Neuronal Cell Lines
- iPSC-derived Cardiomyocytes/Neurons
- Acute/Cultured Organotypic Brain Slices
- Oxygen Glucose Deprivation Model
- 3D Cell Culture
- iPSC-derived Neurons
- Isolation and culture of neural stem/progenitor cells
- Animal Models
- Techinques
- Resource
- Equipment
-
Experiment Systems
- Order
- Careers
CiPA Translational Assays
The third component of CiPA confirms whether the result predicted by the in silico model translates to activity in a phenotypic assay via use of iPSC-derived cardiomyocytes.
Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSC) offer the potential to assess the risk of drug-induced pro-arrhythmia using a human derived model. The potential advantage is that it is possible to have an assay in which cells express a full range of ion channels as expressed in human ventricular myocytes. This approach is unique as cells can be differentiated to express not only normal, but also many variant cardiac disease phenotypes (e.g., LQTs), catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia (CPVT), overlap syndrome of cardiac Na+ channelopathy and arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy (ARVC). The potential for development of drug-induced arrhythmia may be evaluated by analyzing the parameters for each phase of the cardiac AP, as previously described. iPSC cardiac myocytes (iPSC-CM) are currently being investigated for use in drug safety ion-channel evaluations. iPSC-CMs can be cultured to obtain a large number of cells and can be used with manual or automated patch-clamp technology.
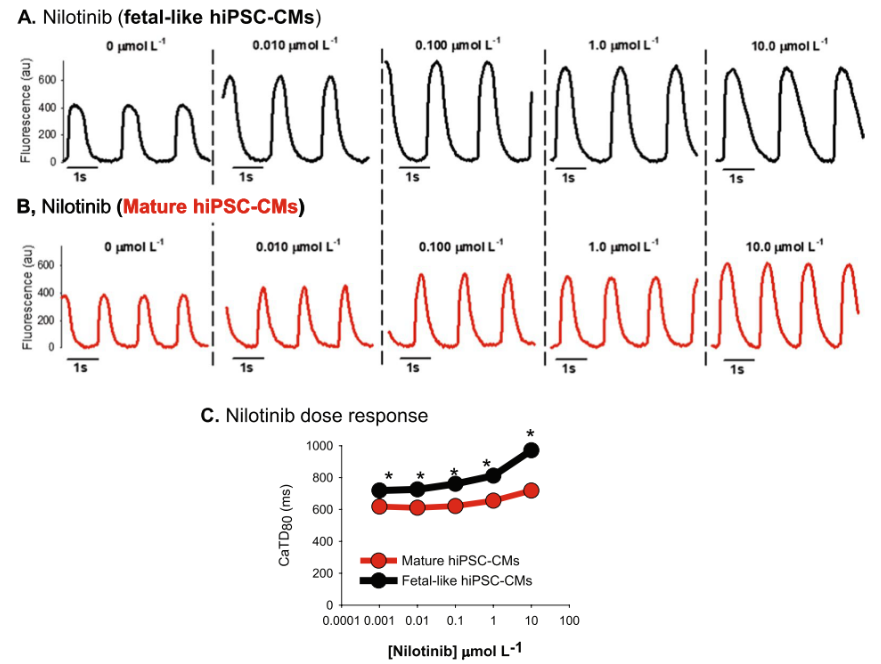
Fig.1 Nilotinib effects on hiPSC-CM intracellular calcium flux
Creative Bioarray can monitor cellular excitability using the microelectrode array (MEA) technique or a dual MEA/impedance readout. Combined with our high-fidelity manual patch-clamp electrophysiology data, the high throughput plate-based output allows us to investigate compound effects on action potentials and membrane currents. We also have a variety of iPSC-derived cardiomyocyte cell lines which have been extensively validated on all phenotypic platforms.
Our MEA analysis combined impedance (IMP, cell contractility) and electrical field potential (EFP) measurements to investigate short-term and long-term pharmacological effects on cardiomyocytes, including beat rate, beating accuracy, amplitude, rise/fall time and pulse width of the IMP signal as well as the amplitude and field potential duration of the EFP signal. The assay provides information on drug-induced alteration or impairment of contractility and EFP of SC-hCMs.
For better evaluating risk and confirming CiPA outcomes, our translational assays of Acrosce CiPA program also include in vivo ECG analysis in both animals (SP CV studies) and humans (phase I clinical trials). Having gained years of experience, Creative Bioarray is capable of providing considerate and reliable services of high quality for our clients. If you have any problems with CiPA test service, do not hesitate to contact us.
Reference
- Monteiro A, et al. hiPSC-CM Monolayer Maturation State Determines Drug Responsiveness in High Throughput Pro-Arrhythmia Screen. Sci Rep. 2017; 7: 13834.
Related Section
Inquiry

