- Home
-
Screening
- Ionic Screening Service
-
Ionic Screening Panel
- Ligand Gated Ion Channels
- Glycine Receptors
- 5-HT Receptors3
- Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors
- Ionotropic Glutamate-gated Receptors
- GABAa Receptors
- Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulators (CFTR)
- ATP gated P2X Channels
- Voltage-Gated Ion Channels
- Calcium Channels
- Chloride Channels
- Potassium Channels
- Sodium Channels
- ASICs
- TRP Channels
- Other Ion Channels
- Stable Cell Lines
- Cardiology
- Neurology
- Ophthalmology
-
Platform
-
Experiment Systems
- Xenopus Oocyte Screening Model
- Acute Isolated Cardiomyocytes
- Acute Dissociated Neurons
- Primary Cultured Neurons
- Cultured Neuronal Cell Lines
- iPSC-derived Cardiomyocytes/Neurons
- Acute/Cultured Organotypic Brain Slices
- Oxygen Glucose Deprivation Model
- 3D Cell Culture
- iPSC-derived Neurons
- Isolation and culture of neural stem/progenitor cells
- Animal Models
- Techinques
- Resource
- Equipment
-
Experiment Systems
- Order
- Careers
Xenopus Oocyte Screening Model
Xenopus laevis (the African clawed frog) oocytes are a popular model system for a wide variety of biological studies. Microinjection of DNA or messenger RNA (mRNA) into the Xenopus oocytes leads to the functional expression of the encoded proteins. The proteins expressed in such a new environment can be functionally characterized under well-defined conditions. This makes oocytes an important expression system for studies of molecular biology and electrophysiology. Such an in vitro expression system is particularly suitable for studying not only the structure and functions of cloned and mutated proteins but also the physiology of neurotransmitter receptors, ion channels, and transporters.
Here in Creative Bioarray, we have automated and manual Xenopus oocyte two-electrode voltage-clamp recordings techniques. Both are useful and important techniques in drug target screening. Although they are not compatible with high-throughput experimentation, these techniques are excellent in combination or as alternatives to fluorescence-based assays for hit validation, screening of focused compound libraries and safety screening on ion channels with their high flexibility for the choice of molecular targets, quality of data and reproducibility.
Advantages
Cost-effective expression system for functional characterization of ion channels
Cells are large, easy to obtain, mechanically and electrically stable and with low expression of endogenous ion channels.
Efficient translation of injected RNA of interest.
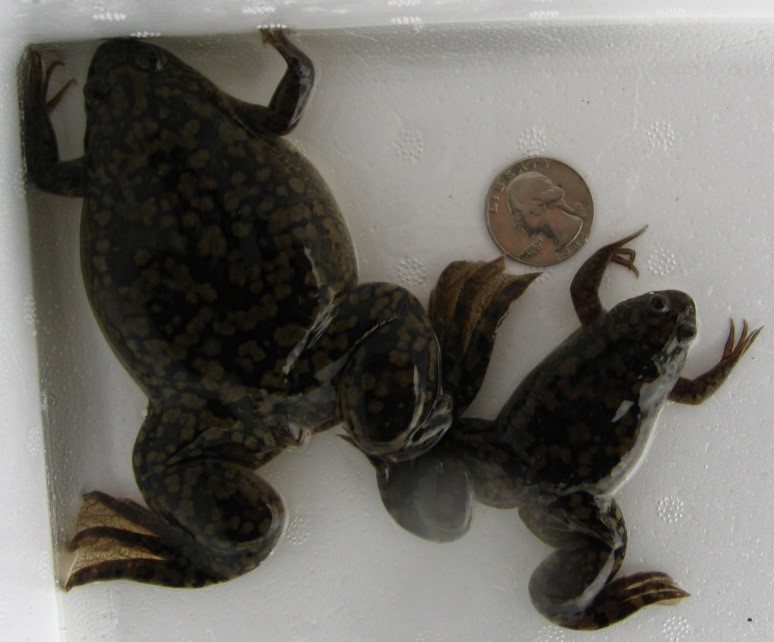

Large amplitude ionic current can be easily recorded using a two-microelectrode whole cell voltage clamp approach. This makes Xenopus oocyte a method of choice not only for screening test compounds to determine their relative efficacies against specific types of ion channels, but also for determining the functional effects of mutations that cause human diseases. Although there are some disadvantages of ion channel screening by Xenopus oocyte - endogenous ion channels expression and different post-translational modification, they are still good ways in ion channels-target screening.
Automated Xenopus oocyte assays in Creative Bioarray offer high quality voltage clamp electrophysiology for drug screening and compound profiling on ion channel targets.
Provides flexible assays with short development time for drug screening and compound profiling.
We offer a broad range of ion channels - Nav, P2X, GABAa and many potassium channels (including hERG) as well as customer specific solutions.
Three fully automated screening systems are available, all equipped with handling robots.
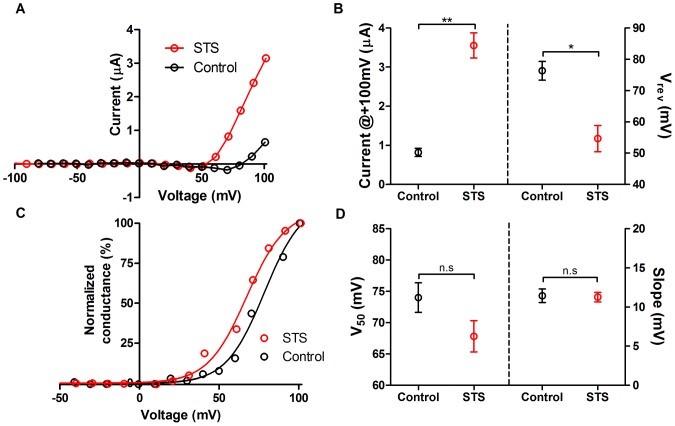
Fig.1 Comparison of Na+ currents in STS-treated and control oocytes
Reference
Englund UH, et al. A Voltage dependent non-inactivating Na+ channel activated during apoptosis in xenopus oocytes. PLoS One. 2014; 9: e88381.
Related Section
- Acute Isolated Cardiomyocytes
- Acute Dissociated Neurons
- Primary Cultured Neurons
- Cultured Neuronal Cell Lines
- iPSC-derived Cardiomyocytes/Neurons
- Acute/Cultured Organotypic Brain Slices
- Oxygen Glucose Deprivation Model
- 3D Cell Culture
- iPSC-derived Neurons
- Isolation and culture of neural stem/progenitor cells
Inquiry

