- Home
-
Screening
- Ionic Screening Service
-
Ionic Screening Panel
- Ligand Gated Ion Channels
- Glycine Receptors
- 5-HT Receptors3
- Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors
- Ionotropic Glutamate-gated Receptors
- GABAa Receptors
- Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulators (CFTR)
- ATP gated P2X Channels
- Voltage-Gated Ion Channels
- Calcium Channels
- Chloride Channels
- Potassium Channels
- Sodium Channels
- ASICs
- TRP Channels
- Other Ion Channels
- Stable Cell Lines
- Cardiology
- Neurology
- Ophthalmology
-
Platform
-
Experiment Systems
- Xenopus Oocyte Screening Model
- Acute Isolated Cardiomyocytes
- Acute Dissociated Neurons
- Primary Cultured Neurons
- Cultured Neuronal Cell Lines
- iPSC-derived Cardiomyocytes/Neurons
- Acute/Cultured Organotypic Brain Slices
- Oxygen Glucose Deprivation Model
- 3D Cell Culture
- iPSC-derived Neurons
- Isolation and culture of neural stem/progenitor cells
- Animal Models
- Techinques
- Resource
- Equipment
-
Experiment Systems
- Order
- Careers
Action Potential Properties
Ventricular repolarization is a complex physiological process determined by the duration of the cardiac action potential (AP). It is the net result of the activities of many highly interdependent membrane ion channels and transporters. The AP is classically divided into 5 phases (0-4). Ion currents, which are outward (upward direction), repolarize the cell or return it to a rested state, whereas ion currents, which are inward (downward in direction), depolarize the cell or excite the cell.
The AP is the sum of over 15 ionic currents, most of which can be altered in the event of QT interval prolongation. This test verifies the direct interaction of all the channels involved in the AP, and can point to the population of channels affected in the event of AP elongation. The APD (AP Duration) assay is useful in detecting and quantifying potentially pro-arrhythmic characteristics such as action potential triangulation, reverse rate-dependence, early-after depolarizations, etc.
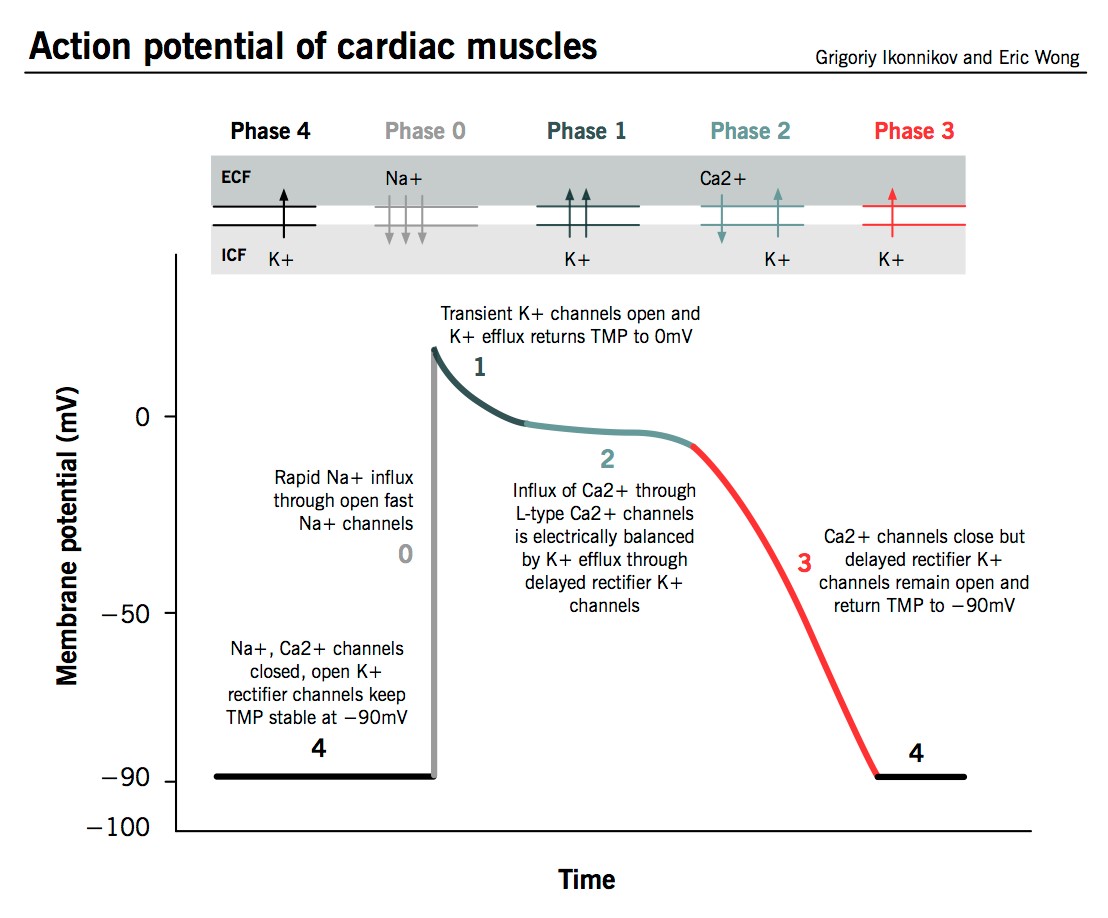
Fig.1 The Action potential of cardiac muscles
As a complementary assessment of in vivo Cardiovascular test, this accurate AP measurement system validated at Creative Bioarray requires a conventional intracellular electrophysiological recording method to assess drug-effects on resting membrane potential, APD, amplitude and maximum rate-of-rise, under near-physiological conditions of ionic composition ([K+] =4 mM), pacing (0.2 Hz, 1 Hz, 2 Hz) and temperature (37.0 ±0.5 ºC). This assay verifies the direct interaction of all the channels involved in AP generation, and can point to the population of channels affected in the characteristics such as rate-dependence and pathological effects such as hypokalemia, hypothermia, etc.
Creative Bioarray provides multiple tissues for test: isolated ventricular strips, trabeculae, papillary muscle, Purkinje fibres or cardiomyocytes. Since Purkinje fibers are thought to be an important site for initiation of arrhythmias, here we give an example of Purkinje fibers.
Purkinje fibers are particularly sensitive to hERG inhibition and therefore to drug-induced prolongation of APD and early after depolarization (EAD). Compared to ventricular muscles, Purkinje fibers may be a better model for studying QT prolongation-related torsade de pointes (TdP). We offer physiologically relevant rabbit whole-ventricle Purkinje fibers preparation for assessment of drug effect on action potential duration. A robust system favorable to the generation of electrical events such as delayed- or early after-depolarizations (EADs) is available in Creative Bioarray.
Advantages
A quantitative assessment of multiple-channel interactions (MICE) with the test article
High-impedance microelectrode impalement
Analytical dissection of the AP in pharmacologically relevant segments: VRest, VMax, dV/dt, APD30, APD60 and APD90, APD90-30
Rate-dependence assessment
Multiple species for evaluation: Rat, guinea-pig, rabbit, dog hearts, etc.
Pre-IND (GLP-compliant) or exploratory designs (non-GLP compliant), FDA-ready hard copy and e-report for electronic IND submission available
Reference
- Ikonnikov G, Yelle D. Physiology of cardiac conduction and contractility. MacMaster Physiological Review, 2014.
Related Section
Inquiry

