- Home
-
Screening
- Ionic Screening Service
-
Ionic Screening Panel
- Ligand Gated Ion Channels
- Glycine Receptors
- 5-HT Receptors3
- Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors
- Ionotropic Glutamate-gated Receptors
- GABAa Receptors
- Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulators (CFTR)
- ATP gated P2X Channels
- Voltage-Gated Ion Channels
- Calcium Channels
- Chloride Channels
- Potassium Channels
- Sodium Channels
- ASICs
- TRP Channels
- Other Ion Channels
- Stable Cell Lines
- Cardiology
- Neurology
- Ophthalmology
-
Platform
-
Experiment Systems
- Xenopus Oocyte Screening Model
- Acute Isolated Cardiomyocytes
- Acute Dissociated Neurons
- Primary Cultured Neurons
- Cultured Neuronal Cell Lines
- iPSC-derived Cardiomyocytes/Neurons
- Acute/Cultured Organotypic Brain Slices
- Oxygen Glucose Deprivation Model
- 3D Cell Culture
- iPSC-derived Neurons
- Isolation and culture of neural stem/progenitor cells
- Animal Models
- Techinques
- Resource
- Equipment
-
Experiment Systems
- Order
- Careers
Isolation and culture of neural stem/progenitor cells
Neural stem cells, with the capacity of self-renewal and abilities to differentiate into the major cell types of the brain, exist in the developing and adult rodent central nervous system. These cells can be grown in vitro for long periods of time while retaining the capacity to differentiate into neurons, astrocytes, and oligodendrocytes.
Creative Bioarray provides both primary neural stem cell and iPSCs for neuroscience research and drug safety evaluation. Here lists some stem cells / culture medium/ iPSC kits we provide:
Stem Cells
Strain C57BL/6 Mouse Neural Stem Cells with GFP
Sprague-Dawley (SD) Rat Neural Stem Cells
Immortalized Human Neural Stem Cells-L-Myc (LM-NSC008)
Arctic Ground Squirrel Neural Stem Cells
QualiCell® Neural Stem Cell-XLC091
QualiCell® Neural Stem Cell-XLC114
…
Cell culture medium
SuperCult® Neural Stem Cells NCR Protein-Free Cryopreservation Medium
SuperCult® Neural Stem Cell Growth Medium
…
iPSC reprogramming Kit
Multiple iPS Cell Reprogramming Kit
We provide services of isolating and expanding neural stem cells in the form of neurospheres from tissue dissections of the embryonic mouse/rat brain. We also provide long-term passage of neurospheres, cryopreservation of neurospheres, and cell differentiation. Our expertise in neural stem cell culture fields guaranteed reliable and consistent results.
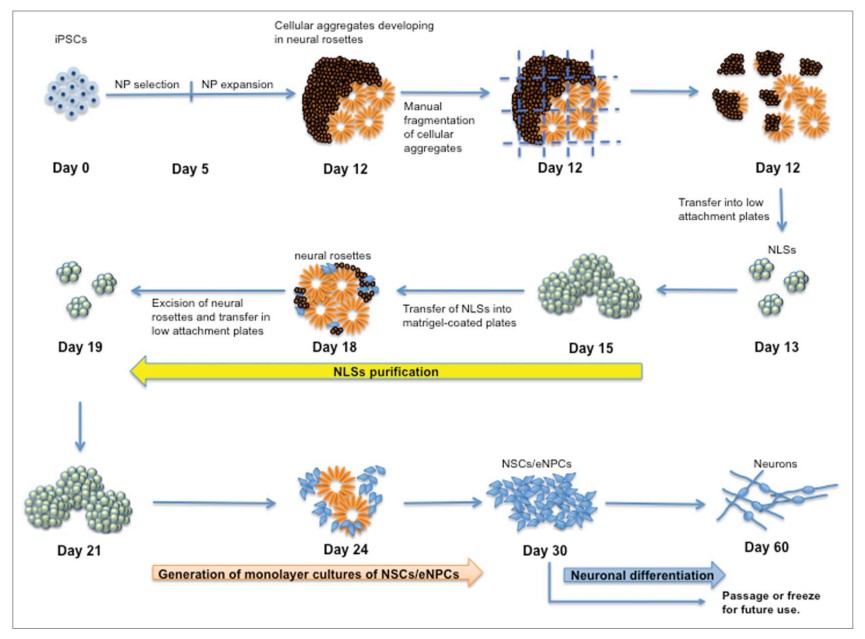
Fig. 1 Schematic flow diagram to depict the stages of differentiation into neurons from induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs). NSCs: neural stem cells; NPCs: neural progenitor cells; NLSs: neurosphere-like structures.
Throughout early development, and continuing into adulthood, stem cells function as reservoirs of undifferentiated cell types whose role is to sustain cell genesis. In the adult, they play an essential homeostatic role by replacing differentiated tissue cells lost by physiological turnover, or lost to injury or disease.
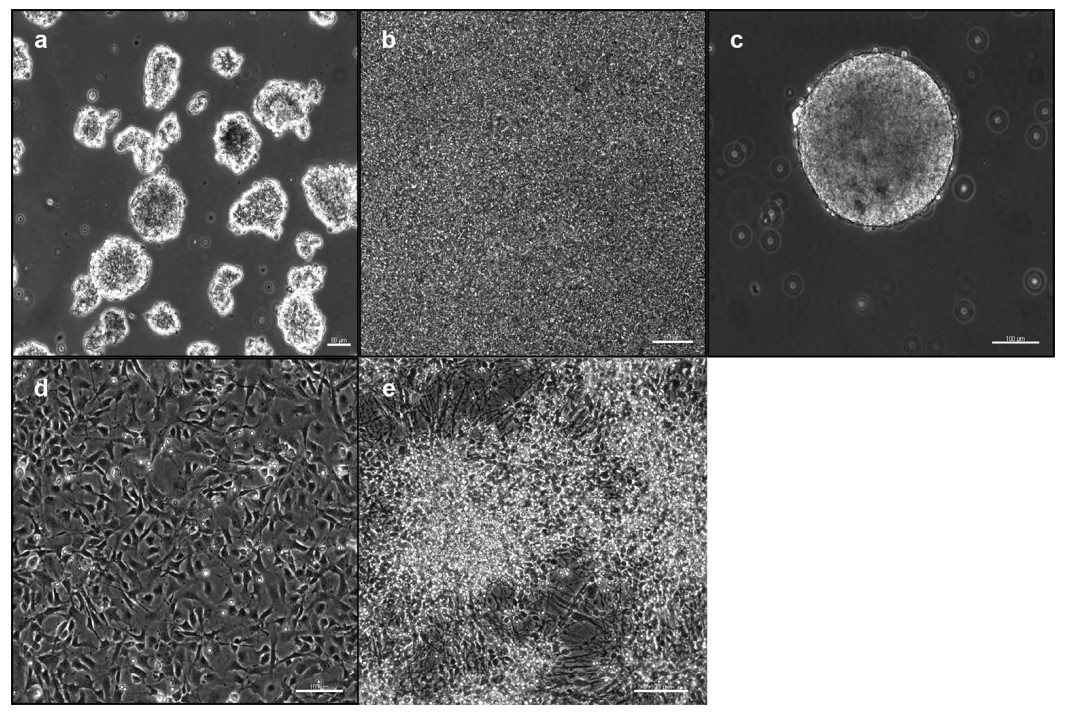
Fig. 2 Induction and cultivation of NSCs from iPSCs: IPSCs were either plated as free-floating EBs
NSC can be cultured as adherent cells, in which they produce large clones containing neurons, glia, and additional stem cells; however, they can also be cultured as floating, multicellular neurospheres. Since the 3D structure of neurosphere creates a niche that is more physiologically relevant than 2D culture systems, neurospheres emerged as the assay of choice and became a scheme for isolating and propagating NSC. Owing to a lack of specific and definitive markers, and poorly defined morphological characteristics, NSC are defined based on functional criterion by what they do rather than by what they look like.
Neural stem cells (NSC), which have the capacity to self-renew and differentiate into the major cell types of the brain, exist in the developing and adult central nervous system (CNS) of all mammals. During development, neuroepithelial germinal cells, described as NSC, proliferate within the ventricular zone and give rise to both neuronal and glial progenitors. In adulthood, new neurons are continually born in predominantly two regions of the brain. The first is the subventricular zone (SVZ), a layer extending along the lateral wall of the lateral ventricle, where NSC and progenitors generate new neurons (neuroblasts) and migrate to the olfactory bulb via the rostral migratory stream. The second region is the subgranular zone (SGZ) of the dentate gyrus of the hippocampus, a thin cell layer between the granule cell layer and dentate hilus.
Neural stem cell is defined as an undifferentiated cell that retains the capacity to the followings. Identification of a stem cell is achieved when all of these criteria are met.
Proliferate
Self - renew (making identical copies of itself)
Become multipotent (generating all the major cell lineages of CNS, including neurons, astrocytes, and oligodendrocytes)
Regenerate tissue after injury
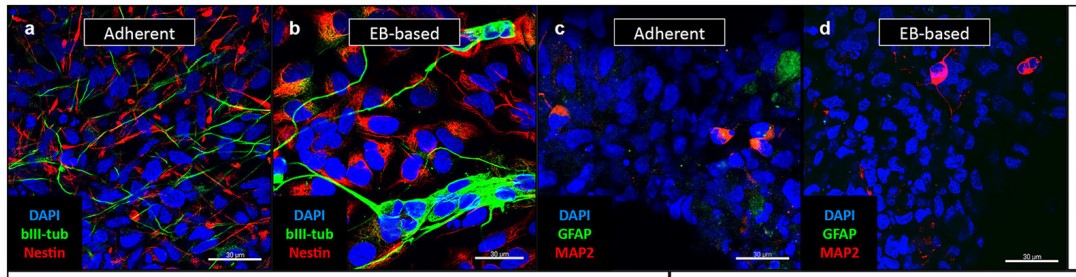
Fig. 3 Immunofluorescence analysis of NSCs under proliferative conditions.
Nevertheless, due to technical or experimental limitations, only some of these criteria may be satisfied in practice. Here at Creative Bioarray, we use the neurosphere formation method to isolate neural stem cells, two central criteria for the definition of a stem cell fulfills: self-renewal and multipotency. We also provide neural stem cell specified culture medium. For customers who need neuronal-derived iPSCs, we offer iPSC reprogramming kit.
In Creative Bioarray, we provide multiple NSCs, the propagation of which can be a source of tissue for many types of applications, from developmental biology to drug screening and cell therapy.
References
Pauly MG, et al. Adherent vs. Free-Floating Neural Induction by Dual SMAD Inhibition for Neurosphere Cultures Derived from Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2018; 6: eCollection 2018.
D'Aiuto L, et al. Large-scale generation of human ipsc-derived neural stem cells/early neural progenitor cells and their neuronal differentiation. Organogenesis. 2014; 10: 365–377.
Xiong, H., & Gendelman, H. E. (Eds.). Current laboratory methods in neuroscience research. Springer. 2014
Related Section
- Xenopus Oocyte Screening Model
- Acute Isolated Cardiomyocytes
- Acute Dissociated Neurons
- Primary Cultured Neurons
- Cultured Neuronal Cell Lines
- iPSC-derived Cardiomyocytes/Neurons
- Acute/Cultured Organotypic Brain Slices
- Oxygen Glucose Deprivation Model
- 3D Cell Culture
- iPSC-derived Neurons
Inquiry

