- Home
-
Screening
- Ionic Screening Service
-
Ionic Screening Panel
- Ligand Gated Ion Channels
- Glycine Receptors
- 5-HT Receptors3
- Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors
- Ionotropic Glutamate-gated Receptors
- GABAa Receptors
- Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulators (CFTR)
- ATP gated P2X Channels
- Voltage-Gated Ion Channels
- Calcium Channels
- Chloride Channels
- Potassium Channels
- Sodium Channels
- ASICs
- TRP Channels
- Other Ion Channels
- Stable Cell Lines
- Cardiology
- Neurology
- Ophthalmology
-
Platform
-
Experiment Systems
- Xenopus Oocyte Screening Model
- Acute Isolated Cardiomyocytes
- Acute Dissociated Neurons
- Primary Cultured Neurons
- Cultured Neuronal Cell Lines
- iPSC-derived Cardiomyocytes/Neurons
- Acute/Cultured Organotypic Brain Slices
- Oxygen Glucose Deprivation Model
- 3D Cell Culture
- iPSC-derived Neurons
- Isolation and culture of neural stem/progenitor cells
- Animal Models
- Techinques
- Resource
- Equipment
-
Experiment Systems
- Order
- Careers
Spontaneous Locomotor Functions
When assessing potential side-effects of investigational compounds, the evaluation of motor function is crucial. Many behavioral tests depend on locomotor activity and animal performance can be influenced by the changes in activity levels. Therefore, it is important to know baseline effects of compounds (or genetic manipulation) on locomotion and related motor functions for proper interpretation of the results. Creative Bioarray offers standard assays for evaluation of locomotor activity for evaluation of motor function.
Fine motor skills' impairment is used as an early marker for diagnosis in muscular degenerative and neurodegenerative diseases. In order to effectively test therapeutic compounds in animal models, it is imperative to characterize the relevant neurodegenerative and muscular degenerative mouse models for fine motor impairment. However, there are limited instruments and assays available to test animal models for fine motor impairment.
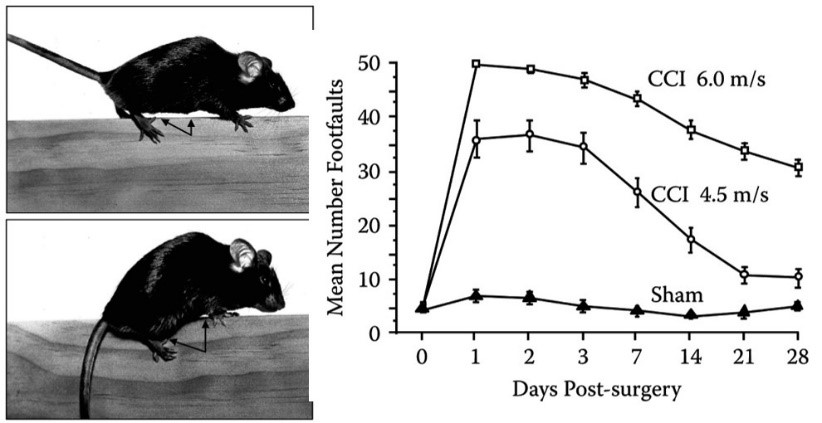
Fig. 1 The effect of moderate controlled cortical impact (CCI) brain injury on beam walking performance for the C57BL/6 mouse
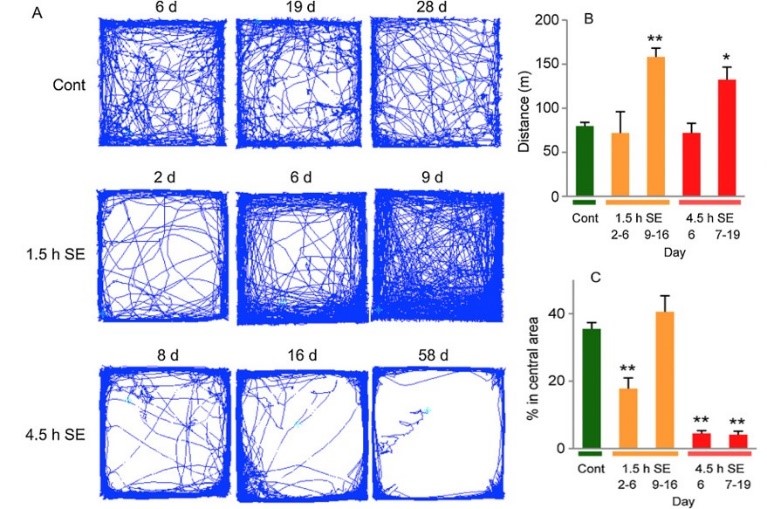
Fig. 2 Time-dependent changes in anxiety-related behavior in the open field test after status epilepticus (SE)
Scientists at Creative Bioarray recently used a series of novel automated and high-precision systems for successfully analyzing fine motor skills in multiple animal models.
For evaluating animal motor functions (spontaneous activities and fine motor functions), we offer:
Open Field Test
Beam Test
Catalepsy (Bar Test)
Dyskinesias
Extrapyramidal Symptoms
Grip Strength
Locomotor Activity (telemetry, beam breaking, wheel running)
Rearing and Climbing
Sedation
Stride length
Video-tracking
Grip Strength
Rearing and Climbing
Righting Reflex
Tapered Beam Test
Running Wheel Activity
Treadmill
Rotarod
Actimeter
MotoRater
Animal-model related (using PD as an example)
Parkinson's dyskinesia ratings
Parkinson's motor testing
References
Otsuka S, et al. Dual mechanisms of rapid expression of anxiety-related behavior in pilocarpine-treated epileptic mice. Epilepsy research. 2016, 123: 55-67.
Curzon P, et al. The Behavioral Assessment of Sensorimotor Processes in the Mouse: Acoustic Startle, Sensory Gating, Locomotor Activity, Rotarod, and Beam Walking. In: Buccafusco JJ (ed). Boca Raton (FL), 2009.
Related Section
- Anxiety-Depression and Social Interaction Evaluation
- Assays for Neuropsychiatric Disorders
- Cognitive Functions
Inquiry

