- Home
-
Screening
- Ionic Screening Service
-
Ionic Screening Panel
- Ligand Gated Ion Channels
- Glycine Receptors
- 5-HT Receptors3
- Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors
- Ionotropic Glutamate-gated Receptors
- GABAa Receptors
- Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulators (CFTR)
- ATP gated P2X Channels
- Voltage-Gated Ion Channels
- Calcium Channels
- Chloride Channels
- Potassium Channels
- Sodium Channels
- ASICs
- TRP Channels
- Other Ion Channels
- Stable Cell Lines
- Cardiology
- Neurology
- Ophthalmology
-
Platform
-
Experiment Systems
- Xenopus Oocyte Screening Model
- Acute Isolated Cardiomyocytes
- Acute Dissociated Neurons
- Primary Cultured Neurons
- Cultured Neuronal Cell Lines
- iPSC-derived Cardiomyocytes/Neurons
- Acute/Cultured Organotypic Brain Slices
- Oxygen Glucose Deprivation Model
- 3D Cell Culture
- iPSC-derived Neurons
- Isolation and culture of neural stem/progenitor cells
- Animal Models
- Techinques
- Resource
- Equipment
-
Experiment Systems
- Order
- Careers
Channelopathies
Channelopathies are diseases caused by disturbed function of ion channel subunits or the proteins that regulate them. Ion channel mutations cause many distinct dysfunctions. Channelopathies under research are basically included in our brief review.
Creative Bioarray is your ideal and reliable innovation partner in research endeavors. We have a comprehensive cell bank with a variety of specialized and unique stable cell lines expression ion channels that can be applied to a variety of in vitro research and in vivo pharmacology study instantly
Featured Content

Achromatopsia
Achromatopsia, also known as rod monochromacy and total congenital color blindness. It is a medical syndrome that usually exhibits at least five related symptoms, such as color blindness, amblyopia, hemeralopia...
Learn More
Benign Familial Neonatal Seizures
Benign familial neonatal convulsions (BFNC) is a rare idiopathic epilepsy syndrome, which is mainly manifested as febrile seizures during the neonatal period, and then disappears spontaneously within a few weeks or months.
Learn More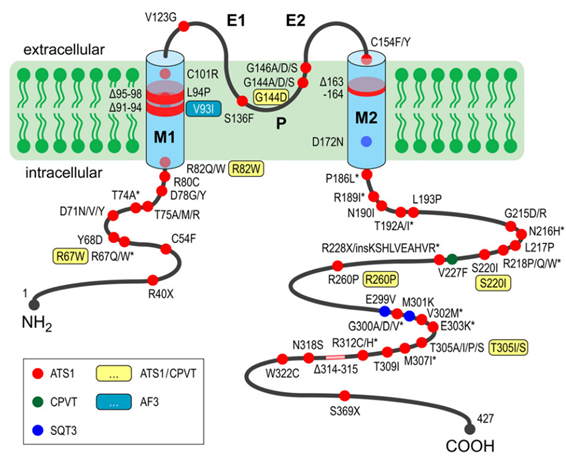
Andersen-Tawil syndrome
Andersen Tawil syndrome (ATS), also known as long QT syndrome type 7 (LQT7), is a rare genetic disease characterized by ventricular arrhythmias, periodic paralysis, and abnormal physiological morphology...
Learn More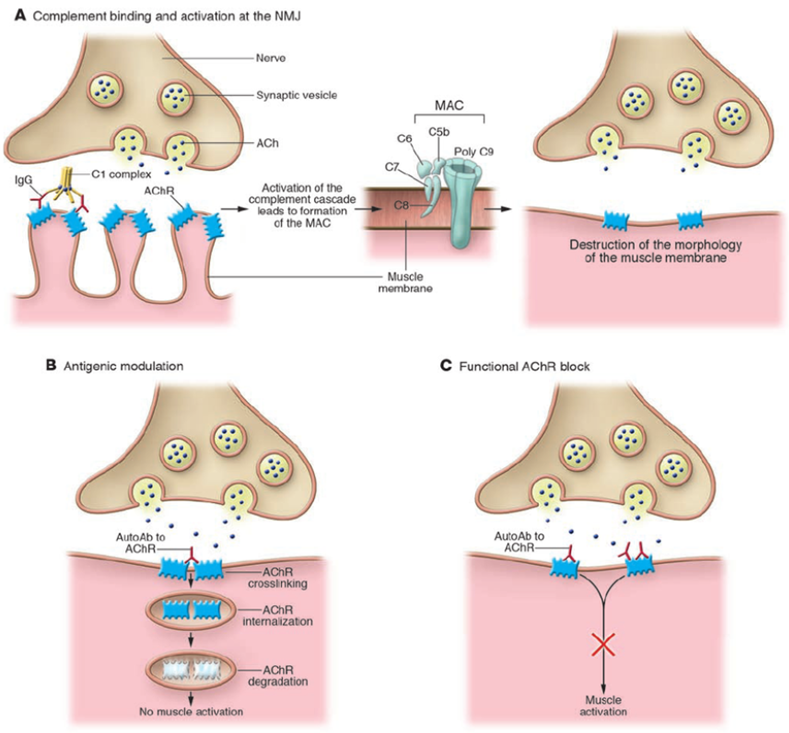
Autoimmune Autonomic Ganglionopathy
Autoimmune autonomic ganglionopathy (AAG) is an immune-mediated acquired autonomic dysfunction disease that is related to auto-acetylcholine receptor antibodies and...
Learn More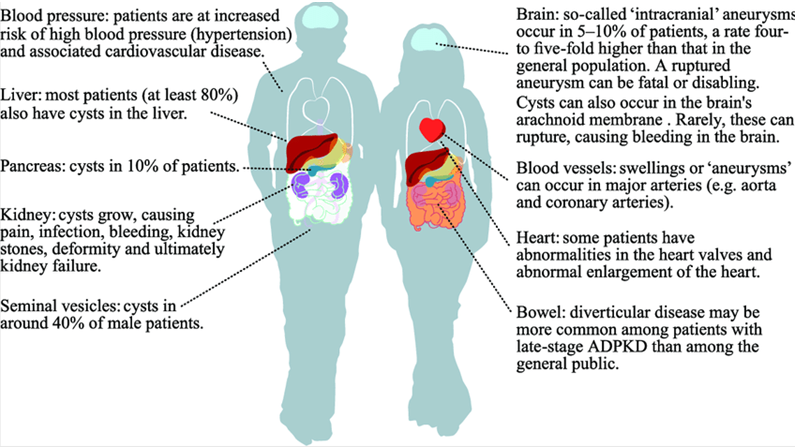
Autoimmune Autonomic Ganglionopathy
Polycystic kidney disease (PKD) is a common autosomal inherited disease, which is single-gene inherited. It is genetically divided into dominant and recessive categories...
Learn More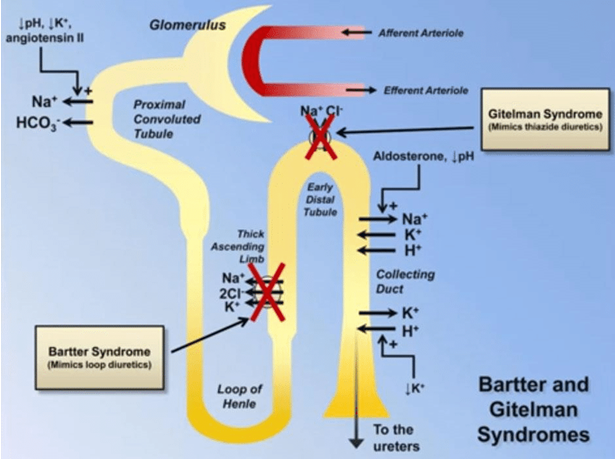
Bartter Syndrome
Bart syndrome (BS) was named after Bartter et al. first reported two cases of hypokalemia metabolic alkalosis, hyperaldosteronism, normal blood pressure, and renal histological...
Learn More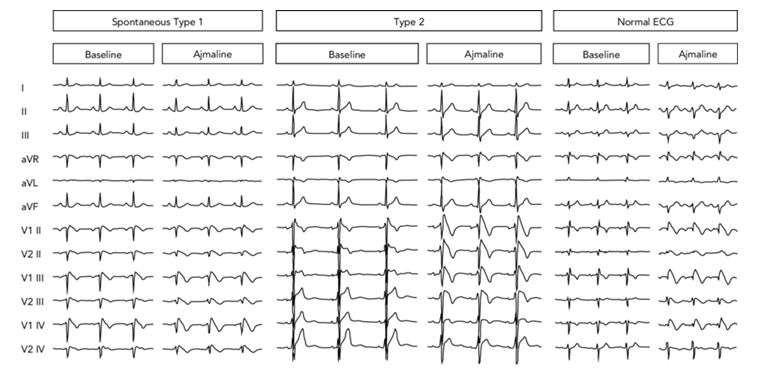
Brugada Syndrome
The Brugada Syndrome (BrS) is a rare autosomal dominant genetic disease. The disease has a normal heart structure, but once the onset will have serious consequences, the main clinical manifestations are cardiogenic syncope...
Learn More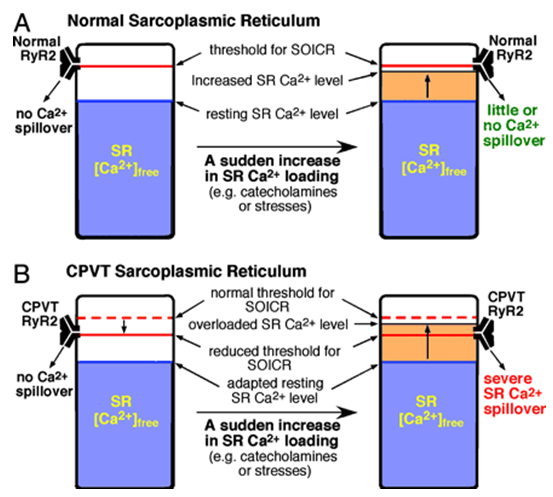
Catecholamine-Sensitive Pleomorphic Ventricular Tachycardia
Catecholamine-sensitive pleomorphic ventricular tachycardia (CPVT) is a primary cardiac electrical disorder that occurs mostly in adolescents with no organic heart disease and a normal QT interval...
Learn More
Andersen-Tawil syndrome
Children absence epilepsy (CAE) is a systemic idiopathic epilepsy, characterized by frequent typical absence seizures, bilateral symmetric synchronized 3 Hz rhythmic spike slow wave discharge...
Learn More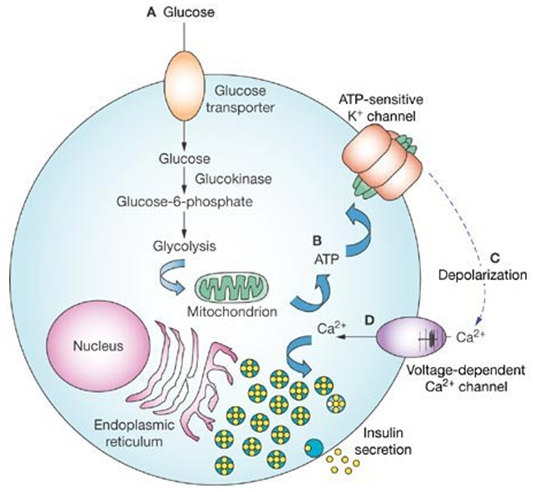
Congenital Hyperinsulinemia
Congenital hyperinsulinism (CHI) is the most common cause of persistent hypoglycemia in infants, so CHI is also known as persistent hyperinsulinemia hypoglycemia in infants. In 1954, MacQuarriet first introduced infantile idiopathic hypoglycemia Report the disease...
Learn More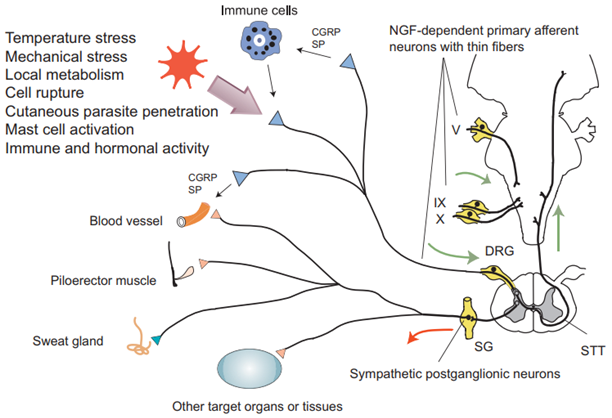
Congenital Insensitivity To Pain
Congenital insensitivity to pain is a genetic disorder of sensory autonomic nervous system. In patients with this type of disease, the transmission of pain is blocked, that is, pain sensation is dull or lost...
Learn More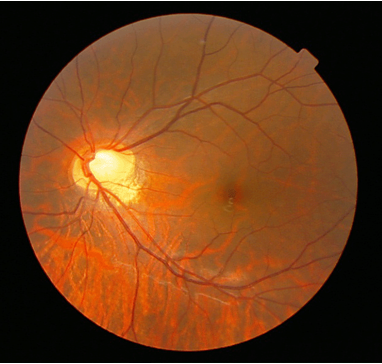
Congenital Stationary Night Blindness
Congenital static night blindness(CSNB) is a type of hereditary ophthalmological disease that mainly damages the function of the retinal rod system. Its clinical characteristics are non-progressive night blindness after birth...
Learn More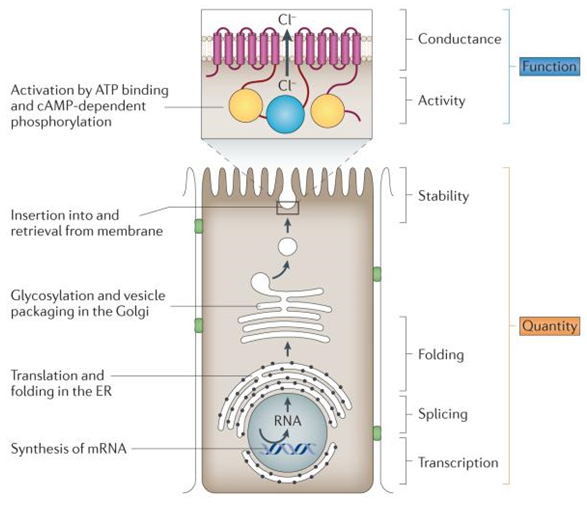
Cystic Fibrosis
Cystic fibrosis (CF) is the most common lethal autosomal recessive disease. It is caused by a gene mutation on autosome No. 7 that encodes the cystic fibrosis transmembrane transcription regulator (CFTR) protein...
Learn More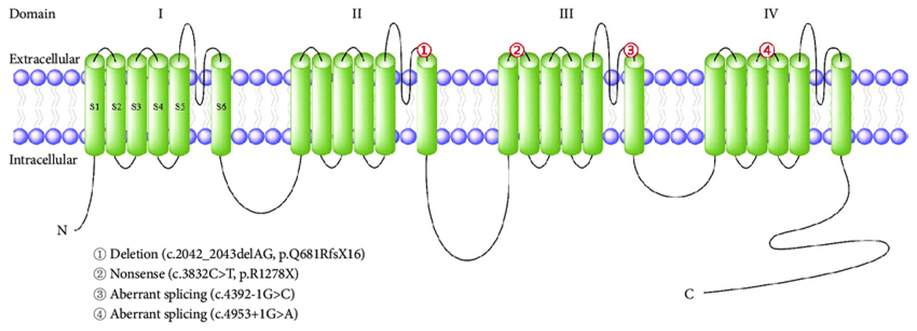
Episodic Ataxia
Episodic ataxia (EA) is a rare type of autosomal dominant genetic disease, mainly manifested as self-limited cerebellar dysfunction with almost no fixed or progressive neurological abnormalities...
Learn More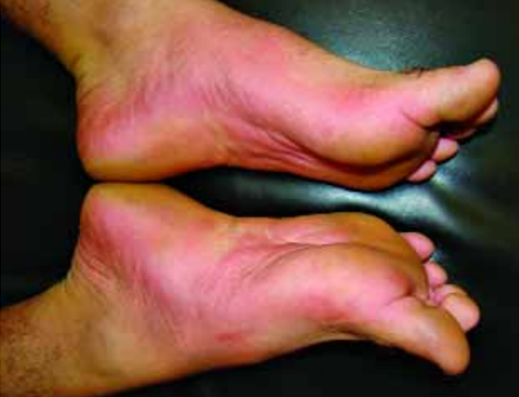
Primary Erythromelalgia
Primary erythromelalgia is an autosomal single-gene genetic disease. Its symptoms are mainly paroxysmal severe burning pain in the distal limbs, increased skin temperature, flushing of the complexion...
Learn More
Familial Atrial Fibrillation
Atrial fibrillation is one of the most common clinical tachyarrhythmias. With the aging of the social population, the incidence of atrial fibrillation is gradually increasing. Its serious complications include cerebral embolism...
Learn More
Familial Hemiplegic Migraine
Migraine is the most common chronic onset headache. About 6% of men and 18% of women in the general population suffer from this disease. According to the 2004 International Headache Society (HIS) classification standard.
Learn More
Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis
Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS) is a pathological diagnosis characterized by partial glomerular segmental scar formation and partial foot process disappearance...
Learn More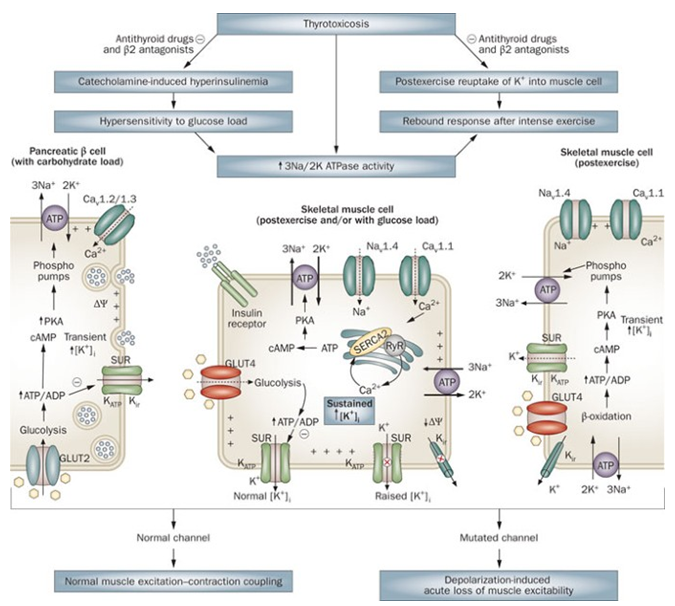
Hypokalemic Periodic Paralysis
When the genes encoding ion channel subunits undergo mutations/expression abnormalities, or pathological endogenous substances appear in the body for the channels, the function of the channels is reduced or enhanced to varying degrees...
Learn More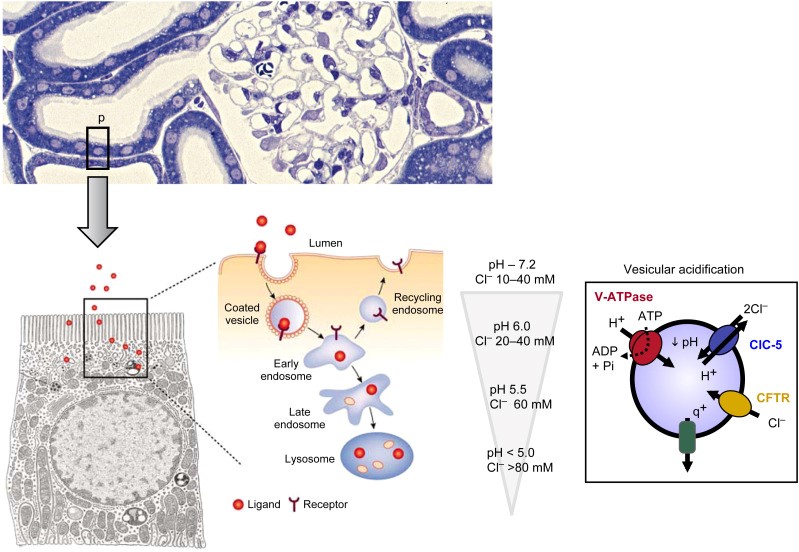
Dent's Disease
Dent disease is an X-linked recessive genetic disease. It was first reported by Dent et al. in 1964. The clinical features include low molecular proteinuria (LWMP)...
Learn More
Generalized Epilepsy with Febrile Seizures Plus
Generalized epilepsy with febrile seizures plus (GEFS+) is a series of seizure disorders with different severity. GEFS+ is usually diagnosed when family members have febrile epilepsy...
Learn More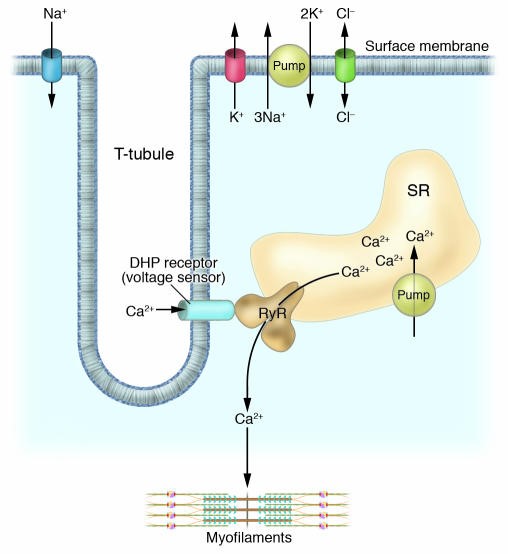
Hyperkalemic Periodic Paralysis
Hyperkalemic periodic paralysis (HYPP) is an autosomal dominant genetic disease. It affects sodium channels in muscle cells and affects the level of potassium particles in the blood...
Learn More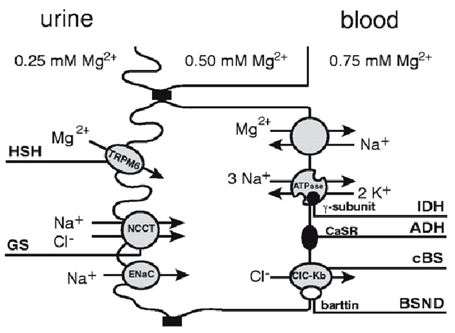
Hypomagnesemia with Secondary Hypocalcemia
Hypomagnesemia with secondary hypocalcemia is a genetic disease caused by the body's inability to absorb and retain magnesium ingested through diet. Because it cannot be stored and absorbed by itself...
Learn More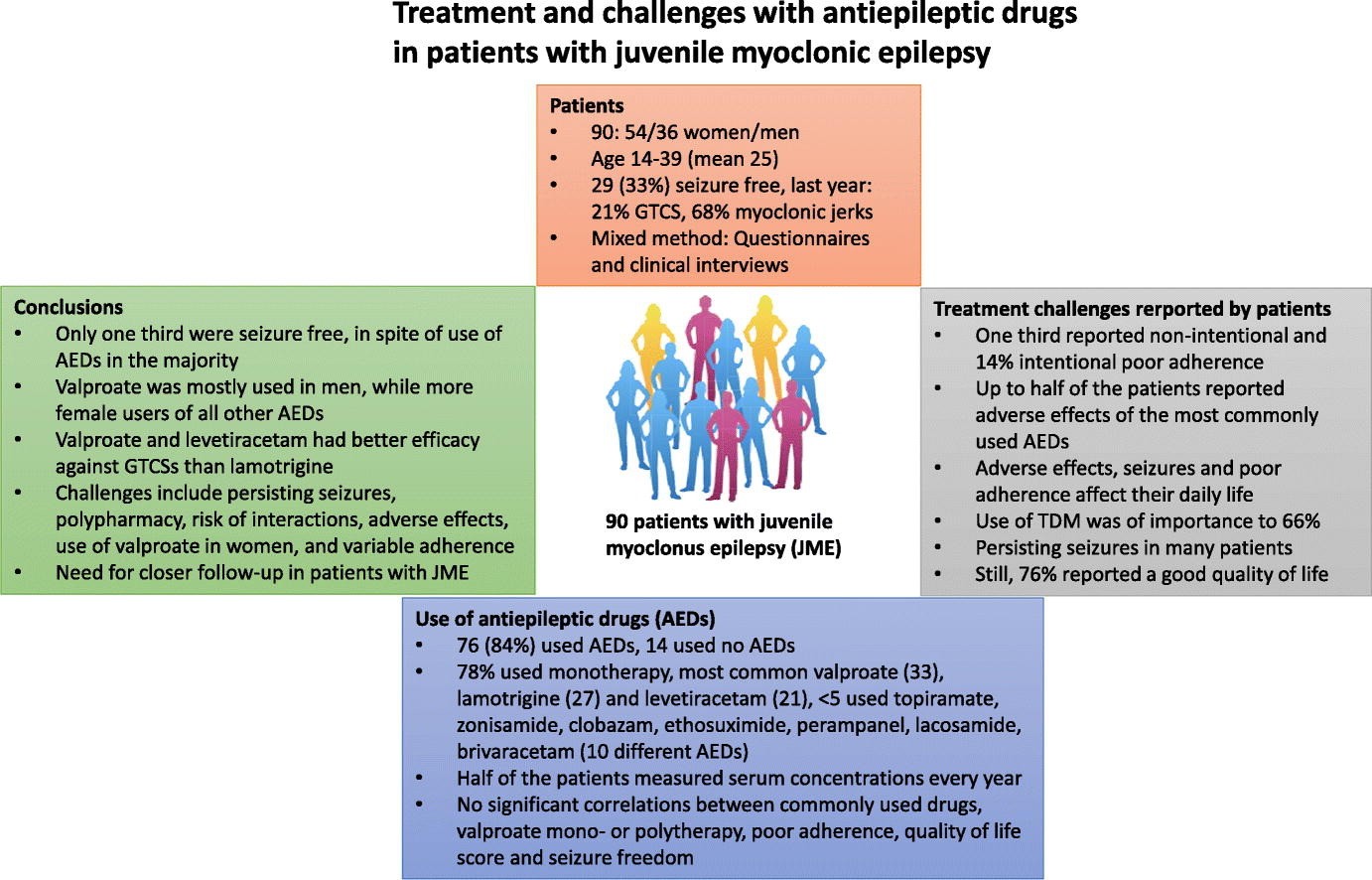
Juvenile Myoclonic Epilepsy
Juvenile myoclonic epilepsy (JME), also known as Janz syndrome, was included in the international classification of epilepsy and epilepsy syndrome in 1989. JME is one of the most common idiopathic (hereditary) and general epilepsy syndromes (IGEs)...
Learn More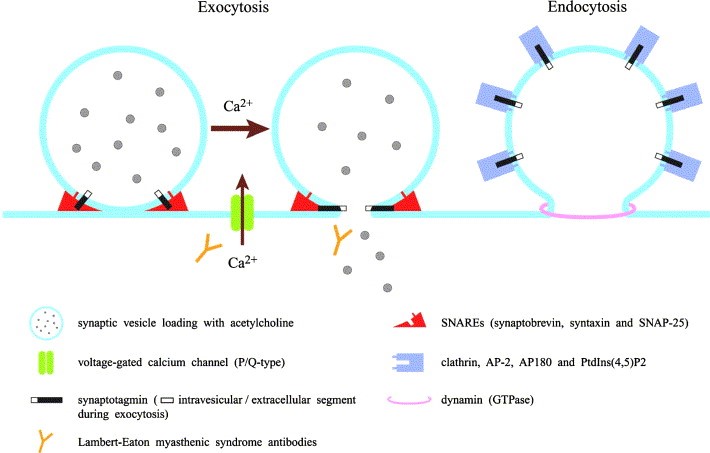
Lambert–Eaton Myasthenic Syndrome
Lambert-Eaton myasthenia syndrome (LEMS) is an autoimmune disease, that is, a disease in which the immune system attacks the body's own tissues. The attack occurs at the junction between the nerve and muscle...
Learn More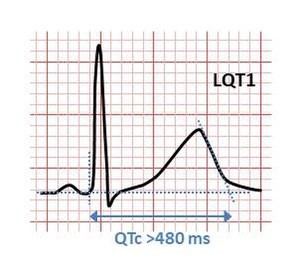
Long QT Syndrome
Long QT syndrome (LQTS) is a disease in which the heart repolarizes after a heartbeat. This can increase the risk of arrhythmia and may even cause fainting, drowning, seizures or sudden death...
Learn More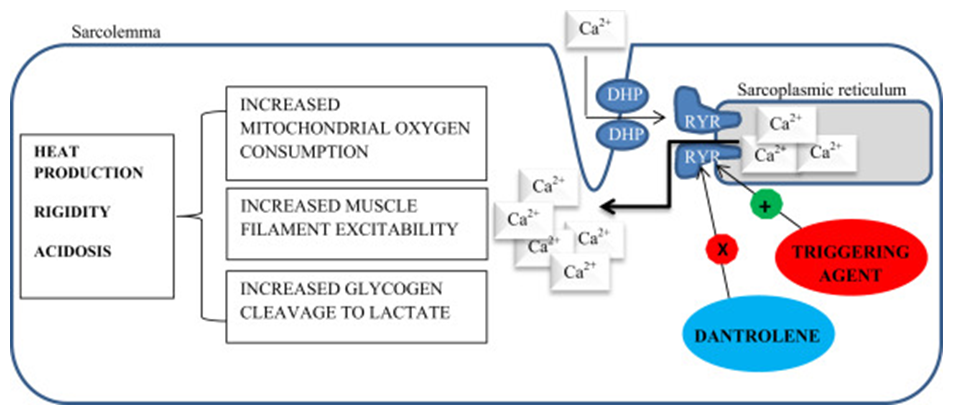
Malignant Hyperthermia
Malignant hyperthermia (MH) is a rare, autosomal-linked genetic disease of the muscular system. It is induced by the commonly used halogenated inhalation anesthetics and depolarizing muscle relaxants (succinylcholine).
Learn More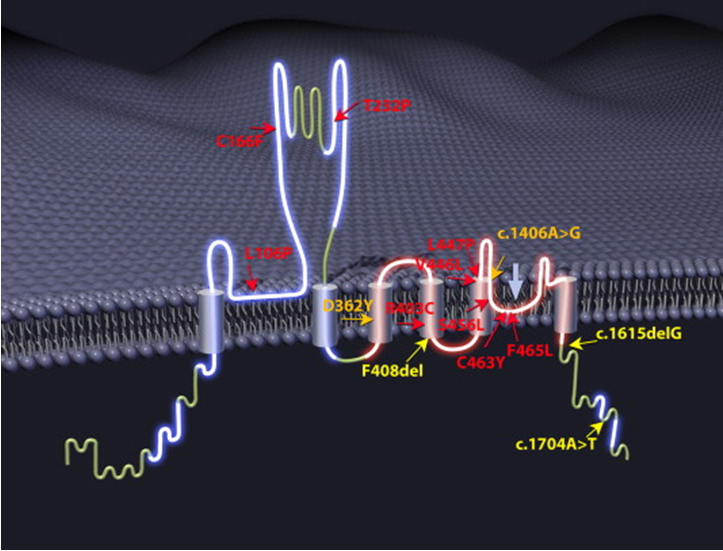
Mucolipidosis Type IV
Mucolipidosis type IV disease is a genetic disease characterized by developmental delay and visual impairment, and symptoms will worsen over time. The severe form of this disease is called typical mucolipidosis type IV disease, while the mild form is called mucolipidosis type IV disease.
Learn More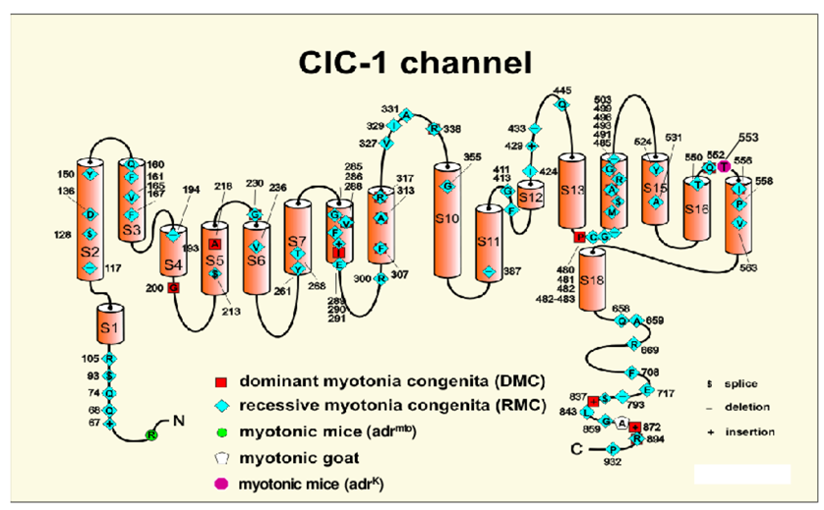
Myotonia Congenita
Myotonic myopathies (MM) is a group of primary/secondary ion channel proteins (Cl-/Na+/Ca2+/K+) structure/function abnormalities, skeletal muscle cell membrane depolarization disorder, and hereditary skeletal muscle diseases with continuous repetitive discharge.
Learn More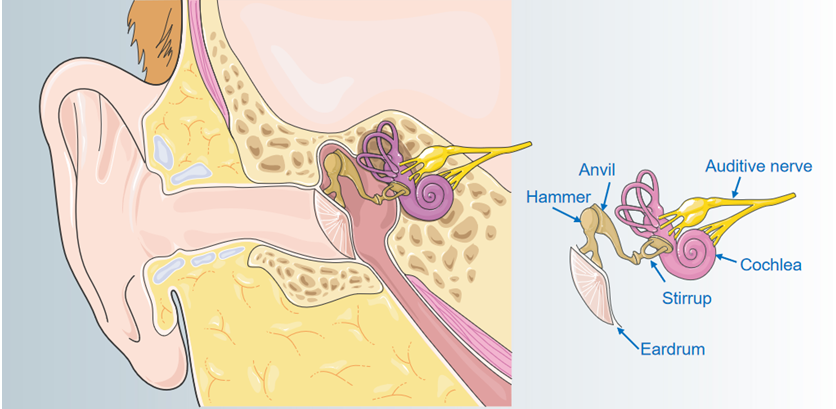
Nonsyndromic Deafness
Deafness is the most common birth defect disease. Hereditary deafness can be divided into two types: one is syndromic hearing impairment (SHI) and the other is non-syndromic hearing impairment (NSHI), and 70% of hereditary deafness manifests as NSHI.
Learn More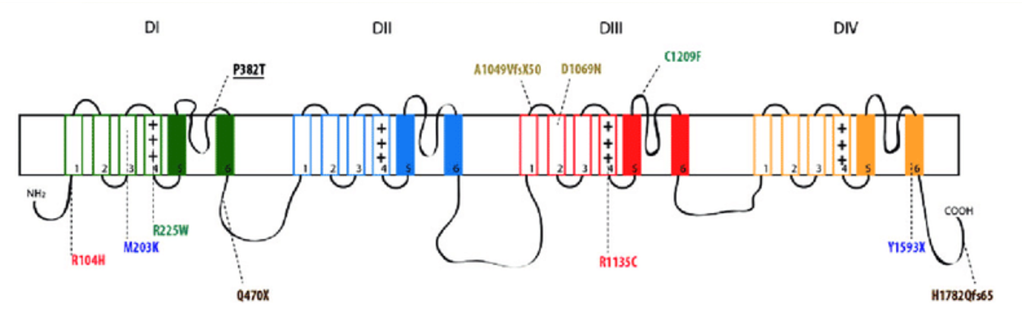
Paramyotonia Congenita
Paramyotonia congenita, also called Eulenburg disease, is a disease that affects muscle (skeletal muscle) movement. It usually occurs in childhood. The main symptom is muscle rigidity, which is often accompanied by muscle weakness, especially after exercise or cold.
Learn More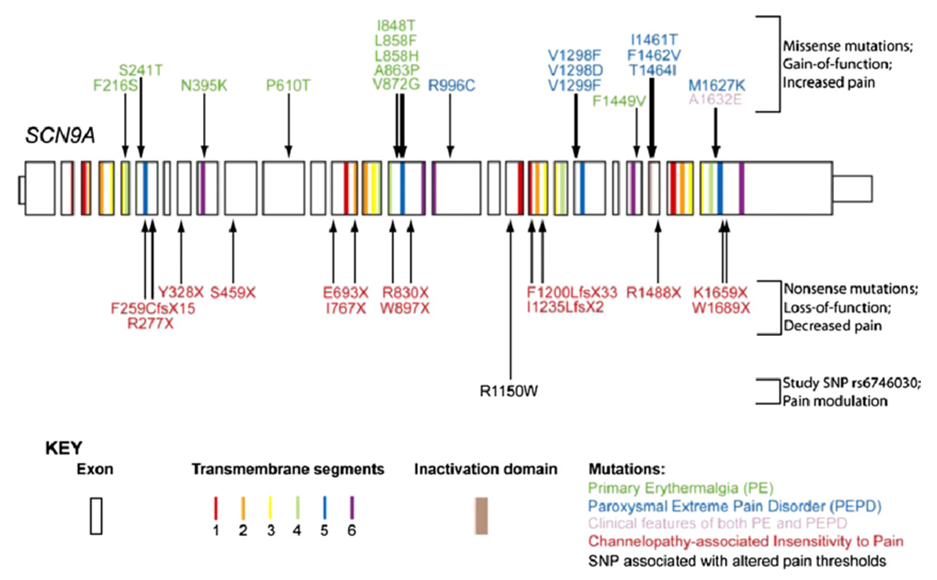
Paroxysmal Extreme Pain Disorder
Paroxysmal extreme pain disorder is a disease characterized by redness and warming (flushing) of the skin, and severe pain in various parts of the body. Among them, the area of redness usually corresponds to the painful part.
Learn More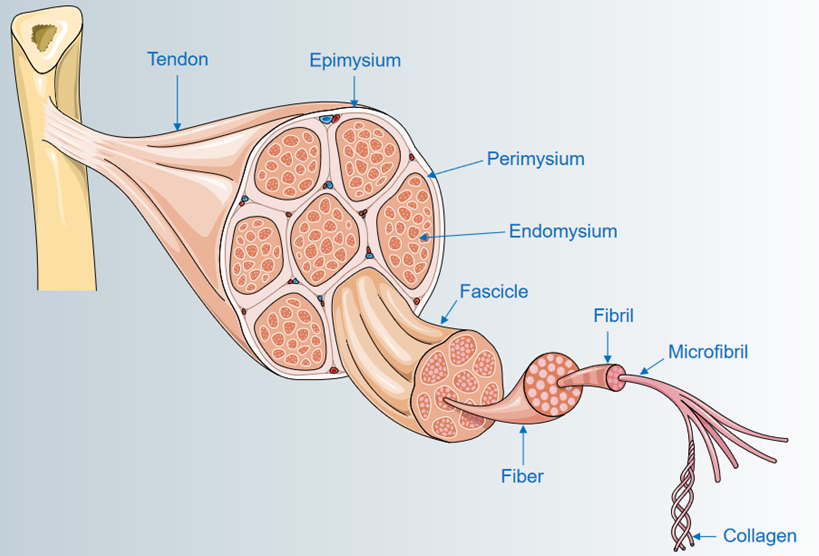
Potassium-aggravated Myotonia
Potassium aggravated myotonia is a disease that affects muscles used for exercise. The disease usually starts in childhood or adolescence. People with this disease will continue to show a continuous burst of muscle tension (muscle stiffness) that prevents the muscles from relaxing normally.
Learn More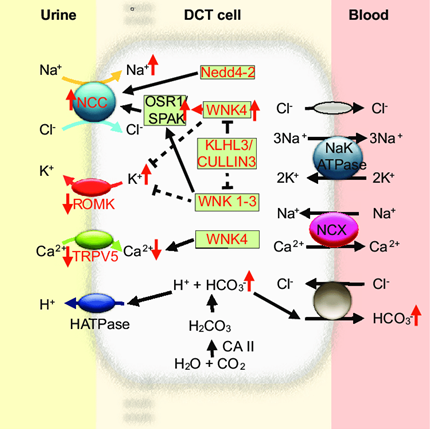
Pseudohypoaldosteronism
Pseudohypoaldosteronism is a disease similar to hypoaldosteronism. Clinically, pseudohypoaldosteronism is divided into two types, namely pseudohypoaldosteronism type 1 and pseudohypoaldosteronism type 2...
Learn More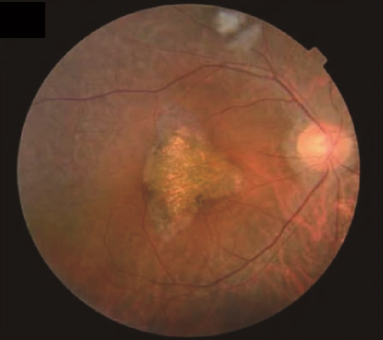
Retinitis Pigmentosa
Retinitis pigmentosa is a group of related eye diseases that cause progressive vision loss. These diseases affect the light-sensitive tissue layer at the back of the eye, the retina. In patients with retinitis pigmentosa, vision loss occurs...
Learn More
Romano-Ward Syndrome
Romano-Ward syndrome is a disease that causes the normal rhythm of the heart (arrhythmia) to be interrupted. This disease is a form of prolonged QT syndrome, which is a type of heart disease that causes the heart...
Learn More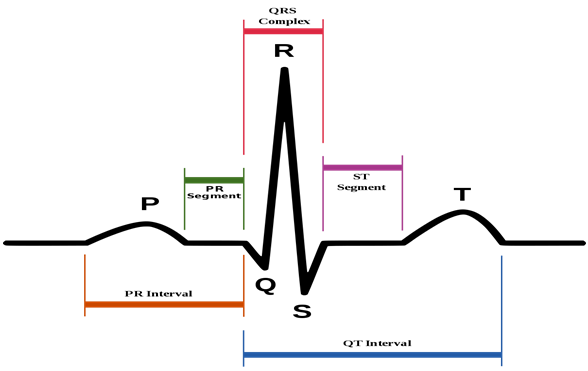
Short QT Syndrome
Short QT syndrome (SQTS) is a disease characterized by a shortened QT interval of the ECG, which shows a high incidence of malignant arrhythmias (ventricular tachycardia/ventricular fibrillation). Among them...
Learn More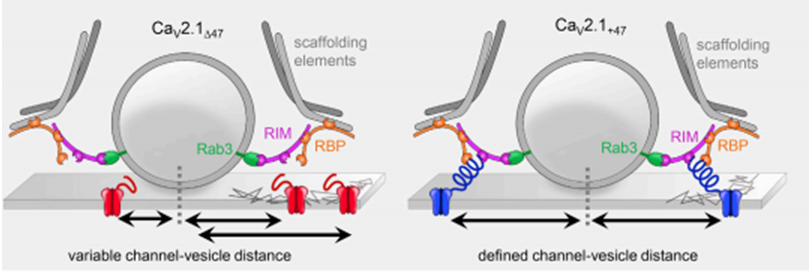
Spinocerebellar Ataxia Type 6
Spinocerebellar ataxia type 6 (SCA6) is an autosomal dominant type of spinocerebellar ataxia. Studies have found that it is related to the trinucleotide CAG repeat of the gene encoding the voltage-gated calcium channel...
Learn More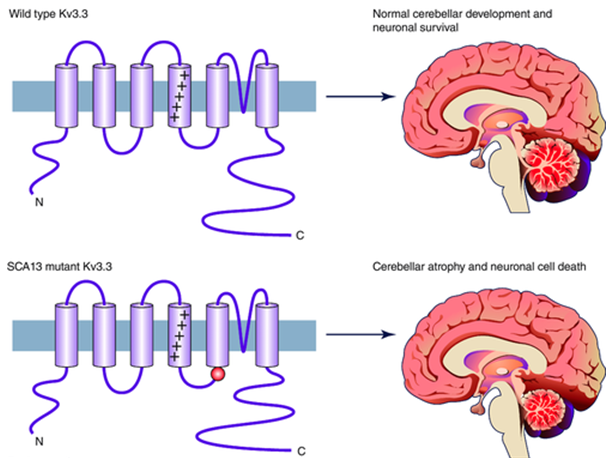
Spinocerebellar Ataxia Type-13
Spinocerebellar ataxia 13 (SCA13) is a rare subtype of spinocerebellar ataxia (SCA), a group of neurological diseases that cause degeneration of the brain and spinal cord. The age of symptoms and the type...
Learn More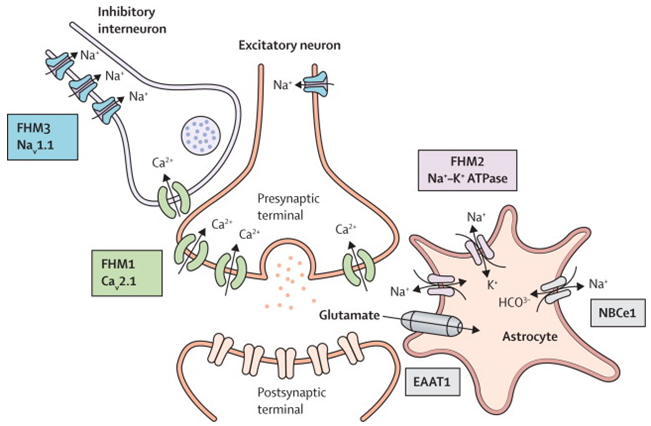
Sporadic Hemiplegic Migraine
Sporadic hemiplegic migraine is a rare form of migraine. Migraine is a symptom that causes severe tic pain in one area of the head. It has been clinically found that some people with migraine also feel nausea...
Learn More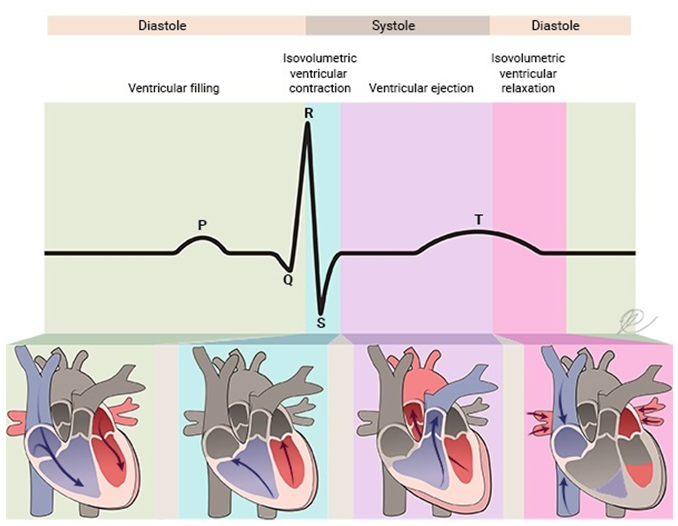
Timothy Syndrome
Timothy syndrome is a rare disease. It mainly affects heart function, but it also affects many other parts of the body, including fingers and toes, teeth, nervous system, and immune system. The severity of the disease varies among...
Learn MoreRelated Section
Inquiry

