- Home
-
Screening
- Ionic Screening Service
-
Ionic Screening Panel
- Ligand Gated Ion Channels
- Glycine Receptors
- 5-HT Receptors3
- Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors
- Ionotropic Glutamate-gated Receptors
- GABAa Receptors
- Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulators (CFTR)
- ATP gated P2X Channels
- Voltage-Gated Ion Channels
- Calcium Channels
- Chloride Channels
- Potassium Channels
- Sodium Channels
- ASICs
- TRP Channels
- Other Ion Channels
- Stable Cell Lines
- Cardiology
- Neurology
- Ophthalmology
-
Platform
-
Experiment Systems
- Xenopus Oocyte Screening Model
- Acute Isolated Cardiomyocytes
- Acute Dissociated Neurons
- Primary Cultured Neurons
- Cultured Neuronal Cell Lines
- iPSC-derived Cardiomyocytes/Neurons
- Acute/Cultured Organotypic Brain Slices
- Oxygen Glucose Deprivation Model
- 3D Cell Culture
- iPSC-derived Neurons
- Isolation and culture of neural stem/progenitor cells
- Animal Models
- Techinques
- Resource
- Equipment
-
Experiment Systems
- Order
- Careers
Pain Model
Medical treatment for pain costs a lot of money and many people lost work productivity cause of it. However, with renewed interest in the subject, Creative Bioarray has developed more refined methods and more promising approaches in investigating of pain study.
Creative Bioarray provides expertise in delivering the first class preclinical research into pain treatment. Our service is particularly around the mechanisms and development of new treatments into neuropathic pain, inflammatory pain and muscle pain. We have a strong ability in developing precisely tailored research packages to target out client's needs. With our experienced experts, Creative Bioarray provides fully assistance from project design to project executing, all the way until data analysis and reporting to advance our clients' progress towards IND approval.
There are many types of pain which can be categorized according to their characteristics or causes: acute pain, inflammatory (often chronic) pain, neuropathic pain, and others. To study these, Creative Bioarray offers high quality tests including using in vitro electrophysiological techniques and in vivo whole animal model by behavior tests. Our test models can be applied for compounds screening or better understanding function by molecular biology techniques. The expert consultant team in Creative Bioarray will always provide expert consultancy in putting together the study proposal you require, and our investigators will then rapidly deliver data of the highest quality to drive forward your research programs.
Pain research in Creative Bioarray includes:
In vitro (from isolated nerves, naïve and modelled animals)
Action potential recording
Dissociated DRG patch-clamp recordings
Slice patch-clamp recordings
In vivo (from both all naïve and modelled animals)
Single fiber recording
Spontaneous and evoked action potentials recording
Single neuron recording (spinal cord/brain)
Creative Bioarray provides various pain assessment methods, which includes, but not limited to:
Biomarker Analysis
INF measurement from plasma and media
IL1-ß from culture media
TNF-a from plasma and media
Muscle Pain assys
Assessment of muscle nociception in anesthetized animals
Behavioral assessment of muscle pain in a lightly anesthetized model
Post-injection sensitization in a lightly anesthetized model
Behavioral assessment in awake animals
Grip force as a model for muscle hyperalgesia
Bite force as a measure for craniofacial muscle hyperalgesia
In Pain study, nociception is the neural response related to noxious stimuli. Many neural systems in the brain and spinal cord (e.g. opiates, neuropeptide Y, serotonin, NMDA, GABA, etc.) are involved. Subtle changes in any of these systems (by pharmacological or genetic manipulation) may lead to changes in the sensitivity or threshold for stimuli. We can assess animal pain by activation of nociceptors, recruitment of central nociceptive pathways, and predictable nocifensive behaviors in animals. Creative Bioarray provides several pain inducing models including:
Nerve Ligation Models of Neuropathic Pain
Chemotherapy-induced neuropathic pain
Chemical-Induced Inflammatory Pain (formalin, carrageenan, Complete Freund's Adjuvant)
Many pain models and biomarkers are available in Creative Bioarray:
Nociceptive Pain
Formalin Induced Paw Licking and Biting in Rats
Acetic Acid Writhing Test in Mice
Hot Plate Model and Plantar Tests
Tail flick Model
Writhing
Inflammatory Pain
Carrageenan induced Inflammation (Paw Volume, Paw Thickness, Thermal Hyperalgesia in rats
CFA induced Thermal Hyperalgesia/Mechanical Hyperalgesia/Allodynia in Rats
Collagen-induced Arthritis (CIA) in DBA Mice
Neuropathic Pain Models (nerve injury, diabetic neuropathy, chemotherapy, fracture, etc.)
CCI-induced Neuropathic Pain in Rats (Bennet & Xie model)
L5/L6 Ligation-induced Neuropathic (Chung's Model)
Streptozotocin (STZ)-induced Diabetic Neuropathy in Rats
Chemotherapy (Paclitaxel) induced Neuropathic pain
Target Engagement
Coupled with Biomarker Analysis for in vitro- in vivo correlation and Human Dose projection
Migraine
Visceral pain
Surgical pain
Muscle pain
Intramuscular injection (algogens, bolus and intramuscular infusion)
Ischemic contraction
Novel or prolonged exercising
Mechanical stimulation
Electrical stimulation
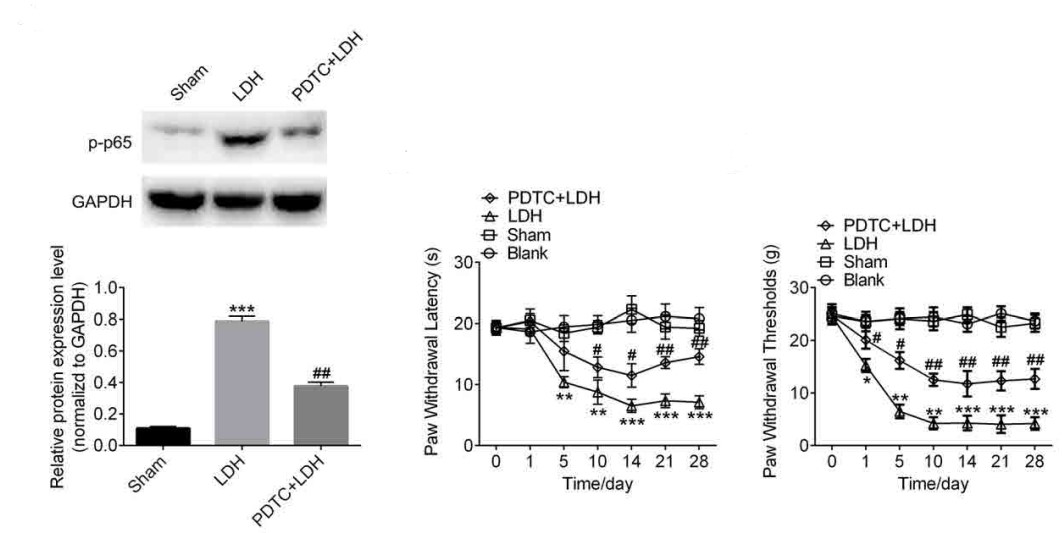
Fig. 1 Downregulation of NF-κB attenuates LDH-Induced neuropathic pain.
Experimental animals for pain study need special consideration because ethical issues. We have professional and experienced experts to handle those complicated technical and ethical problems, and help our clients to reach research goals. We provide specialized knowledge to help our clients develop the most feasible and reliable mode in pain study. We will work closely with you to obtain the most effective and meaningful data from pain study using animal model.
Reference
Liu C, et al. NF-κB mediated CX3CL1 activation in the dorsal root ganglion contributes to the maintenance of neuropathic pain induced in adult male Sprague Dawley rats. Acta Cir Bras. 2018; 33: 619–628.
Related Section
- Alzheimer's Disease Model
- Parkinson's Disease Model
- Huntington's Disease Model
- Epilepsy Model
- ALS Model
- Psychiatric Model
- Autism Spectrum Disorder
- Cerebral-Spinal Injury Model
- Stroke Model
- Fragile X Model
- Acute/Chronic Heart Failure Model
Inquiry

