- Home
-
Screening
- Ionic Screening Service
-
Ionic Screening Panel
- Ligand Gated Ion Channels
- Glycine Receptors
- 5-HT Receptors3
- Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors
- Ionotropic Glutamate-gated Receptors
- GABAa Receptors
- Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulators (CFTR)
- ATP gated P2X Channels
- Voltage-Gated Ion Channels
- Calcium Channels
- Chloride Channels
- Potassium Channels
- Sodium Channels
- ASICs
- TRP Channels
- Other Ion Channels
- Stable Cell Lines
- Cardiology
- Neurology
- Ophthalmology
-
Platform
-
Experiment Systems
- Xenopus Oocyte Screening Model
- Acute Isolated Cardiomyocytes
- Acute Dissociated Neurons
- Primary Cultured Neurons
- Cultured Neuronal Cell Lines
- iPSC-derived Cardiomyocytes/Neurons
- Acute/Cultured Organotypic Brain Slices
- Oxygen Glucose Deprivation Model
- 3D Cell Culture
- iPSC-derived Neurons
- Isolation and culture of neural stem/progenitor cells
- Animal Models
- Techinques
- Resource
- Equipment
-
Experiment Systems
- Order
- Careers
fEPSP / Populational Spikes Recordings
Extracellular recording is a classical electrophysiological technique that continues to be a widely used and powerful tool in neuroscience research. Recording the electrical activity of individual nerve, glial and muscle cells is important in research and clinical settings.
Although there are some disadvantages including immeasurable cell membrane potential (technically difficult to record, often not feasible and, indeed, frequently not necessary) and the signals recorded extracellularly are usually small and difficult to detect, the electrophysiological recording technique remains as one of the most popular methods in modern neuroscience research in detecting neuronal transmission functions.
Creative Bioarray provides the service including recording fEPSP and PS, along with the analysis and interpretation of the data. Due to the extensive usage of the rodent hippocampal slices in neuroscience studies, recordings of field potentials and compound action potentials on hippocampal brain slices are given as an example to illustrate detailed methods for extracellular recording ex vivo. In addition to intra-cellular (sharp electrode) and whole-cell patch recordings, the evoked and/or spontaneous activities in hippocampal slices can be studied via extracellular recording techniques.
Advantages
In contrast to intracellular recording techniques, extracellular recordings have the advantage of stability and flexibility, making the technique applicable to a wide range of research projects.
Field potential recordings have the best resolution in laminar, densely packed structures, such as the hippocampus, and thus are useful for examining firing behaviors and for determining slice viability.
Because they reflect the synchronous activity of many neurons, extracellular recordings also allow information about the coordinated synaptic activity in a population of neurons to be obtained. With detailed anatomical information about the brain areas that are being recorded from, it is helpful to understand the input–out-put function determining the transformation of information in a neuronal network.
Two most commonly recorded activities in response to electrical stimuli include field excitatory postsynaptic potentials (fEPSP, also termed as FP) evoked from dendritic areas and population spike (PS) which is a sum of action potentials near the somata and commonly with larger amplitude than FP if the recorded somata and dendrites are in the same group.Variations of these techniques have been developed to provide estimates of intracellular events as well as, in most cases, sequences of action potentials. In the latter application, it is most often the event of an action potential occurring at a particular time instant that is of importance, and not its amplitude or shape.
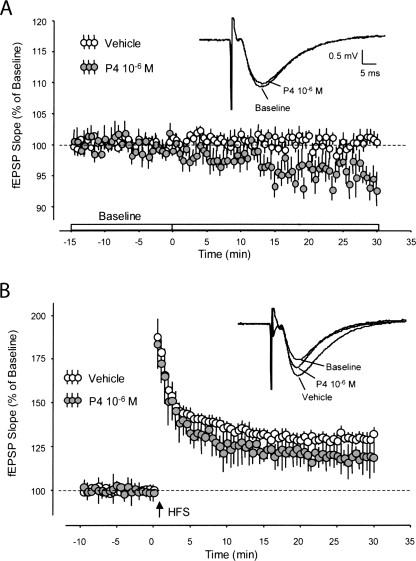
Fig.1 fEPSP baseline synaptic transmission and LTP with progesterone.
All of these recordings can be carried out either in vivo on anesthetized or awake animals, ex vivo on brain slices or dissected fasciculus of spinal cord or nervous trunk, or in vitro in cultured embryonic neuronal tissue field Excitatory Postsynaptic Potential.
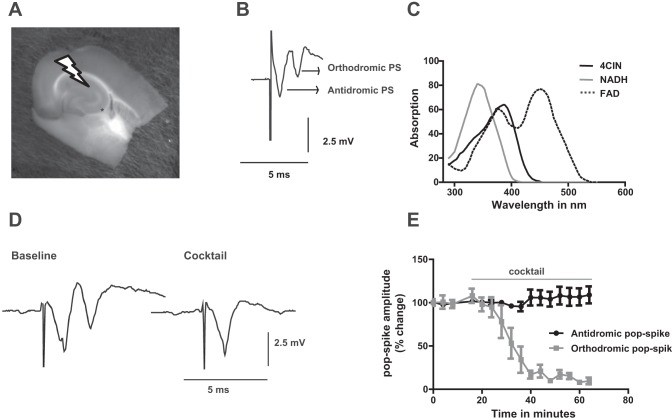
Fig. 2 Sample trace of field potential responses. The 1st component stands for antidromic population spike (PS) while the 2nd one represents orthodromic population spike
If you have any special needs in our fEPSP / Populational Spikes Recordings services, please contact us at Email or Telephone for this special service. Let us know what you need and we will accommodate you according to your project. We look forward to working with you in the future.
References
Foy MR, et al. Progesterone regulation of synaptic transmission and plasticity in rodent hippocampus. Learning & Memory. 2008;15(11):820-822.
Angamo EA, et al. A neuronal lactate uptake inhibitor slows recovery of extracellular ion concentration changes in the hippocampal CA3 region by affecting energy metabolism. Journal of Neurophysiology. 2016;116(5):2420-2430.
Related Section
Inquiry

