- Home
-
Screening
- Ionic Screening Service
-
Ionic Screening Panel
- Ligand Gated Ion Channels
- Glycine Receptors
- 5-HT Receptors3
- Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors
- Ionotropic Glutamate-gated Receptors
- GABAa Receptors
- Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulators (CFTR)
- ATP gated P2X Channels
- Voltage-Gated Ion Channels
- Calcium Channels
- Chloride Channels
- Potassium Channels
- Sodium Channels
- ASICs
- TRP Channels
- Other Ion Channels
- Stable Cell Lines
- Cardiology
- Neurology
- Ophthalmology
-
Platform
-
Experiment Systems
- Xenopus Oocyte Screening Model
- Acute Isolated Cardiomyocytes
- Acute Dissociated Neurons
- Primary Cultured Neurons
- Cultured Neuronal Cell Lines
- iPSC-derived Cardiomyocytes/Neurons
- Acute/Cultured Organotypic Brain Slices
- Oxygen Glucose Deprivation Model
- 3D Cell Culture
- iPSC-derived Neurons
- Isolation and culture of neural stem/progenitor cells
- Animal Models
- Techinques
- Resource
- Equipment
-
Experiment Systems
- Order
- Careers
Ion Channel Functional Assays
Ion channels act as molecular transistors. Powered by ion concentration gradients, ion channels transduce a variety of signals into transmembrane ion fluxes. Ion channels have traditionally been classified according to the mechanisms that control opening-closing transitions (gating) and the types of ions that can pass through a channel (selectivity). These functional characteristics, along with control of expression and localization, determine the effector activities of each channel type. Classification of ion channels based on functional characteristics has been, in large part, supported by sequence analysis of cloned channels and by available structural studies.
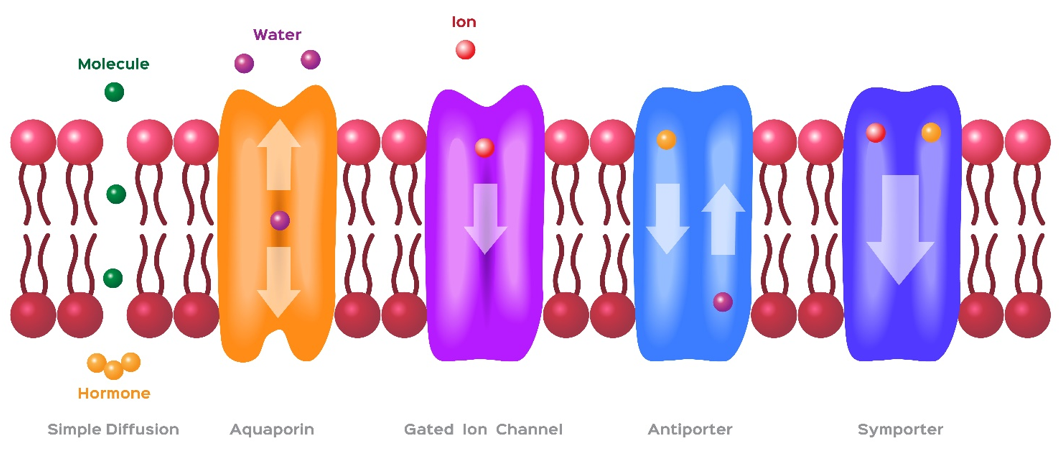
Figure 1 Membrane transporters
Gating and Selectivity Affect Assays
Conventional voltage clamp methods are often used in early stages of ion channel drug discovery and assay development to characterize factors that control channel gating and to determine ion selectivity. This information can then be used to design assays in higher density formats that afford higher throughput at the expense of reduced flexibility, control and resolution.
Fluorescence Assays
Fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) with the use of a pair of dyes, a phospholipid-anchored coumarin and a hydrophobic oxanol that rapidly redistributes in the membrane according to the transmembrane field, can provide robust and reproducible signals when studying the activity of voltage-gated sodium, potassium and other channels. Indeed, the assay can be tuned to identify either activators or inhibitors of a given ion channel.
Ion Flux Assays
Early work in this area was primarily focused on radionuclide-based flux assays. The development of ion-selective fluorescent dye-based indicators revolutionized the measurement of ion flux. These indicators improved the ease of use, as well as spatial and temporal resolution of ion flux measurements. Genetically encoded ion flux indicators including the chemiluminescent calcium sensor, aequorin and a variety of engineered fluorescent proteins are consecutively utilized. The use of automated flame photometry-based ion flux assays has been proven effective as an alternative to fluorescent and radionuclide-based techniques for some ion channel assays.
High-throughput Screening Assays
Ion channels are excellent targets for a wide range of health conditions. Traditional screening method is labor-intensive with a low throughput. The rapid progress in developing functional assays and instrumentation has enabled high throughput screening (HTS) campaigns on an expanding list of channel types. But here are many parameters to consider in optimizing HTS assays, like cell growth and harvesting parameters, cell plating conditions, types of fluorescent dyes for cell based ion flux assays, types of quenching agents, and several other parameters.
Our Ion Channel Screening Services
▪ Assay development and transfer services to compliment your current study design.
▪ Ion channel selectivity profiling.
▪ High-quality, well-characterized ion channel stable cell lines. Most researchers express ion channels in either Chinese Hamster Ovary (CHO) or Human Embryonic Kidney (HEK) cells.
▪ Custom cell line generation – single alpha subunits to more complex multi-subunit combinations, constitutive and inducible expression vectors.
▪ Access to fluorescence-activated cell sorting.
▪ Cell-based functional assays for different ion channels, including:
- Voltage-gated channels (e.g., sodium, potassium and calcium channels),
- Ligand-gated channels (e.g., GABA, nAChR and TRP channels).
▪ Hit-to-lead and lead optimization support using conventional electrophysiology and high throughput screening technologies.
▪ Quick turnaround times of 1-3 weeks depending on project types.
References
- Owen B McManus, Ph.D., et al. Ion Channel Screening. Assay Guidance Manual [Internet]. 2012.
- Yu, Hb., Li, M., Wang, Wp. et al. High throughput screening technologies for ion channels. Acta Pharmacol Sin 37, 34–43 (2016).
Related Section
Inquiry

