- Home
-
Screening
- Ionic Screening Service
-
Ionic Screening Panel
- Ligand Gated Ion Channels
- Glycine Receptors
- 5-HT Receptors3
- Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors
- Ionotropic Glutamate-gated Receptors
- GABAa Receptors
- Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulators (CFTR)
- ATP gated P2X Channels
- Voltage-Gated Ion Channels
- Calcium Channels
- Chloride Channels
- Potassium Channels
- Sodium Channels
- ASICs
- TRP Channels
- Other Ion Channels
- Stable Cell Lines
- Cardiology
- Neurology
- Ophthalmology
-
Platform
-
Experiment Systems
- Xenopus Oocyte Screening Model
- Acute Isolated Cardiomyocytes
- Acute Dissociated Neurons
- Primary Cultured Neurons
- Cultured Neuronal Cell Lines
- iPSC-derived Cardiomyocytes/Neurons
- Acute/Cultured Organotypic Brain Slices
- Oxygen Glucose Deprivation Model
- 3D Cell Culture
- iPSC-derived Neurons
- Isolation and culture of neural stem/progenitor cells
- Animal Models
- Techinques
- Resource
- Equipment
-
Experiment Systems
- Order
- Careers
GPCR Stable Cell Line
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), or seven transmembrane receptors (7TMs), are the largest family of cell-surface molecules involved in signal transduction. GPCRs have drawn much attention for treating hypertension, neurological, pain and other disorders, as more than 40% of the clinically marketed drugs are targeting GPCRs.
GPCR drug screening is essentially based on testing available molecule libraries. Such libraries can contain thousands of different compounds derived either by natural sampling, random synthesis or both, which are tested for their ability to bind to or interfere with the function of a GPCR molecule. Given the large number of molecules in those libraries, the use of high-throughput screening technologies that enable rapid testing through miniaturization and parallelization is indispensable. Creative Bioarray offers a comprehensive selection of binding and functional GPCR assays to meet the GPCR drug discovery research needs of both chemists and biologists. As a pioneer in this field, we can save your time and cost of the discovery programs by taking advantage of our expertise and innovative technology platforms.
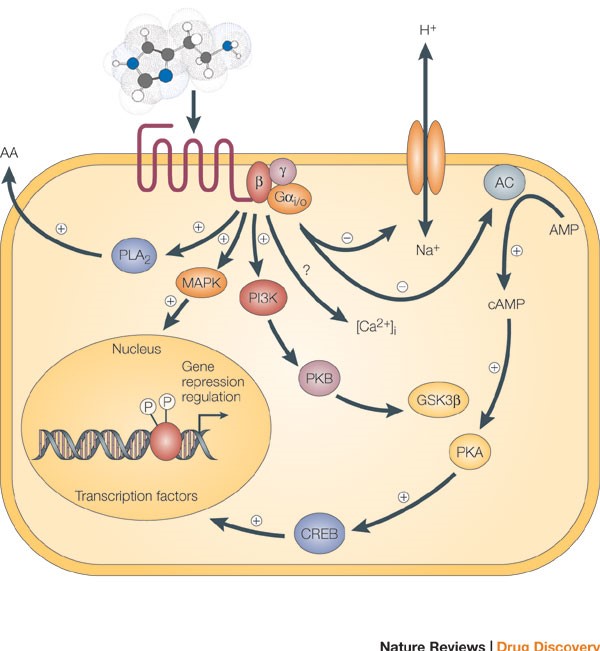
Fig.1 Signaling cascades within a cell can interact to affect multiple molecules in the cell, leading to secretion of substances from the cell, ion channel opening, and transcription
So far, Creative Bioarray has successfully constructed GPCR over-expressing stable cell lines of various species, which has become one of the world's largest banks of GPCR cells. These cell lines have been verified in the functionality and stability through reporter gene assay or intracellular calcium assay, to satisfy our customers' requirements for screening GPCR-target drugs and final evaluation.
Advantages
- One-stop service: Customized cell generation project is managed by experienced scientists throughout the process, from construction design to drug screening.
- Experienced: Creative Bioarray has a professional research team with experience of many years in the field of molecular and cell biology.
- Broad cell types: Creative Bioarray has successfully constructed GPCR over-expressing stable cell lines with HEK293, CHO, HeLa, 1321N1, U2OS, RH7777 etc.
- Genetic stability: Our GPCR over-expressing cell lines have been rigorously tested and validated for at least 10 passages continuous culture without significant change in assay window.
- High Quality: Our GPCR over-expressing cell lines have no mycoplasma contamination.
- Cost & Time saving: There are a lot of choices for premade GPCR stable cells enabling for long-term screening, and ready-to-assay/division-arrested GPCR cells suitable for small scale screening assays.
Reference
Leurs, R. et al. The histamine H3 receptor: from gene cloning to H3 receptor drugs. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery. 2005; 4: 107-120.
Related Products
- Overexpression Cell Line
| Catalog | Product Name | Gene Name | Species | Morphology | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACC-RG0809 | Human CNR1 Stable Cell Line-CHO | CNR1 | Human | Epithelial-like | INQUIRY |
| ACC-RG0810 | Rat Cnr1 Stable Cell Line-CHO | Cnr1 | Rat | Epithelial-like | INQUIRY |
| ACC-RG0815 | Rat Cnr2 Stable Cell Line-CHO | Cnr2 | Rat | Epithelial-like | INQUIRY |
| ACC-RG0819 | Human CCKAR Stable Cell Line-CHO | CCKAR | Human | Epithelial-like | INQUIRY |
| ACC-RG0821 | Human CCKBR Stable Cell Line-CHO | CCKBR | Human | Epithelial-like | INQUIRY |
| ACC-RG0823 | Human CCR2 Stable Cell Line-CHO | CCR2 | Human | Epithelial-like | INQUIRY |
| ACC-RG0831 | Human OPRD1 Stable Cell Line-CHO | OPRD1 | Human | Epithelial-like | INQUIRY |
| ACC-RG0834 | Human S1PR1 Stable Cell Line-CHO | S1PR1 | Human | Epithelial-like | INQUIRY |
| ACC-RG0838 | Human EDNRA Stable Cell Line-CHO | EDNRA | Human | Epithelial-like | INQUIRY |
| ACC-RG0840 | Human EDNRB Stable Cell Line-CHO | EDNRB | Human | Epithelial-like | INQUIRY |
Related Section
- Ion Channel Expressing Cell
- Other Membrane Receptors/Transporters/Exchangers Expression Cell
- Customized Ionic Channel Expression System
Inquiry

