- Home
-
Screening
- Ionic Screening Service
-
Ionic Screening Panel
- Ligand Gated Ion Channels
- Glycine Receptors
- 5-HT Receptors3
- Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors
- Ionotropic Glutamate-gated Receptors
- GABAa Receptors
- Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulators (CFTR)
- ATP gated P2X Channels
- Voltage-Gated Ion Channels
- Calcium Channels
- Chloride Channels
- Potassium Channels
- Sodium Channels
- ASICs
- TRP Channels
- Other Ion Channels
- Stable Cell Lines
- Cardiology
- Neurology
- Ophthalmology
-
Platform
-
Experiment Systems
- Xenopus Oocyte Screening Model
- Acute Isolated Cardiomyocytes
- Acute Dissociated Neurons
- Primary Cultured Neurons
- Cultured Neuronal Cell Lines
- iPSC-derived Cardiomyocytes/Neurons
- Acute/Cultured Organotypic Brain Slices
- Oxygen Glucose Deprivation Model
- 3D Cell Culture
- iPSC-derived Neurons
- Isolation and culture of neural stem/progenitor cells
- Animal Models
- Techinques
- Resource
- Equipment
-
Experiment Systems
- Order
- Careers
Potassium Channels
Potassium channels are the most widely distributed type of ion channel and are present on almost every cell type. Potassium channels can be divided into 4 main classes:
Voltage-gated (Kv)
Inwardly rectifying (Kir)
Tandem-pore domain (K2P)
Calcium-activated (KCa)
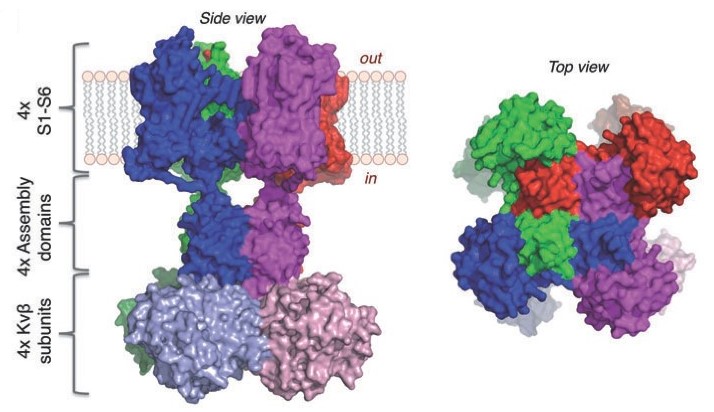
Fig. 1 Structure of Voltage-gated K+ channels (Kv1.2/Kv2.1)
Voltage-gated potassium channel plays an important role in the rapid repolarization of fast-firing brain neurons. The channel opens in response to the voltage difference across the membrane, forming a potassium-selective channel through which potassium ions pass in accordance with their electrochemical gradient. The voltage-gated potassium channels are responsible for firing sustained trains of very brief action potentials at high frequency in pallidal neurons. Of particular importance in the field of drug safety are the voltage-gated potassium channels Kv11.1 (hERG) and Kv7.1 (KCNQ1) which are associated with the potentially fatal Long QT Syndrome.
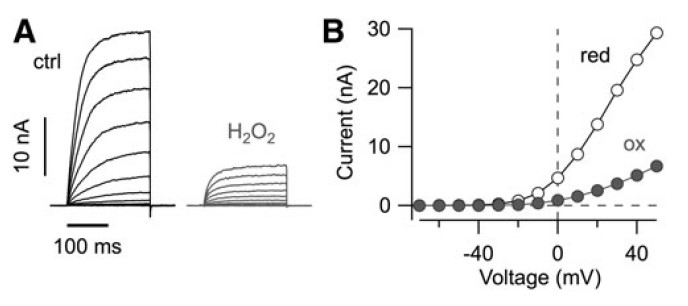
Fig. 2 Voltage-activated K+ channels.
Here at Creative Bioarray, we provide drug targets screening on all following K+ channels. You can customize all your projects and contact our experienced scientists.
Kv1.1 (KCNA1)
Disease: mutations in KCNA1 cause several congenital disorders including episodic ataxia type 1, neuromyotonia and autosomal dominant hypomagnesia.
Therapeutic Targets: multiple sclerosis, stroke and seizure.
Kv1.2 (KCNA2)
Therapeutic Targets: multiple sclerosis.
Kv1.3 (KCNA3)
Description: the upregulation of Kv1.3 channels contributes to the activation of T-lymphocytes during inflammatory reactions.
Therapeutic Targets: multiple sclerosis, cancer, obesity, diabetes, asthma and autoimmune diseases.
Kv1.4 (KCNA4)
Therapeutic Targets: neuropathic pain treatment.
Kv1.5 (KCNA5)
Disease: inherited form of atrial fibrillation.
Therapeutic Targets: atrial fibrillation, pulmonary hypertension, cancer and multiple sclerosis.
Kv1.6 (KCNA6)
Description: displays outward rectification, with fast activation and slow inactivation kinetics at depolarized potentials.
Kv2.1 (KCNB1)
Therapeutic Targets: arrhythmia, in action potential prolongation.
Kv4.3 (KCND3)
Therapeutic Targets: atrial fibrillation.
Kv4.3/KChIP (KCND3/KCNIP2)
Therapeutic Targets: atrial fibrillation.
Kv7.1 (KCNQ1)
Therapeutic Targets: aberrant QT syndromes and cardiac arrhythmia.
Kv7.1/mink (KCNQ1/MINK)
Therapeutic Targets: long QT syndrome.
Kv7.2 (KCNQ2)
Disease: neonatal type-1 epilepsy.
Therapeutic Targets: seizures, convulsions, migraines, dementia, bipolar disorder and neuropathic pain.
Kv7.3 (KCNQ3)
Therapeutic Targets: in the treatment of epilepsy, dementia, bipolar disorder and neuropathic pain.
Kv7.2/Kv7.3 (KCNQ2/KCNQ3)
Disease: mutations in KCNQ2 or KCNQ3 reducing M-current amplitude are responsible for some forms of benign familial neonatal seizure.
Therapeutic Targets: in seizure, stroke, migraine, dementia, bipolar disorder, anxiety and neuropathic pain.
Kv11.1/hERG (KCNH2)
Disease: upregulated in some types of cancer and may serve as a tumor marker. KCNH2 mutations cause inherited forms of cardiac disorders including both long QT (loss-of-function) and short QT (gain-of-function) syndromes. Inhibition of hERG channels by pharmaceuticals is the primary cause of acquired long QT syndrome and drug-induced Torsade de Pointes (TdP). Therapeutic Targets: anti-target in cardiac risk assessment.
Reference
Sahoo N, et al. Oxidative Modulation of Voltage-Gated Potassium Channels. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2014; 21: 933–952.
Related Products
- Overexpression Cell Line
Related Section
- Ligand Gated Ion Channels
- Glycine Receptors
- 5-HT Receptors3
- Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors
- Ionotropic Glutamate-gated Receptors
- GABAa Receptors
- Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulators (CFTR)
- ATP gated P2X Channels
- Voltage-Gated Ion Channels
- Calcium Channels
- Chloride Channels
- Sodium Channels
- ASICs
- TRP Channels
- Other Ion Channels
Inquiry

